Aubrie Henspeter: Leading Commercial Lunar Missions
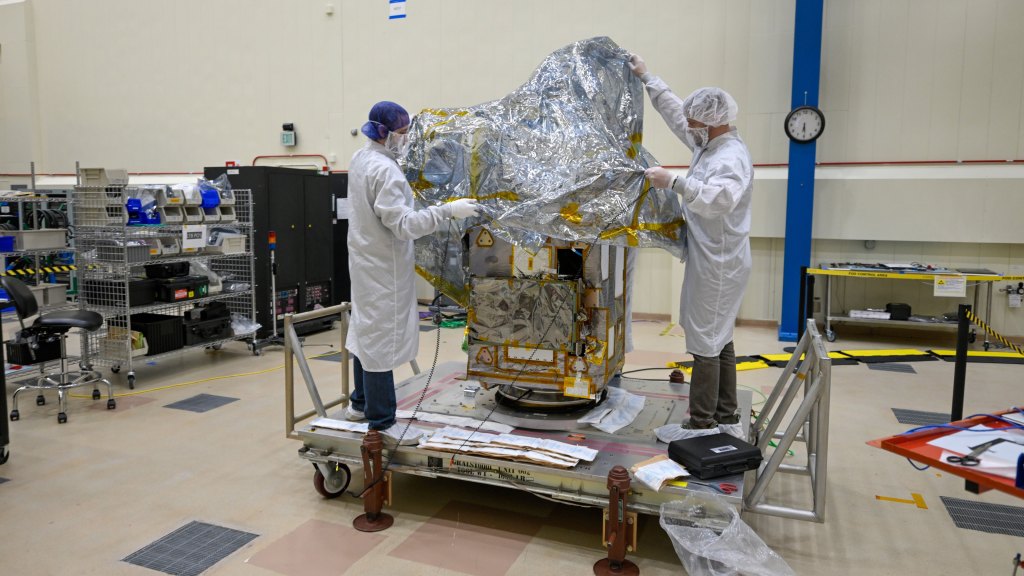
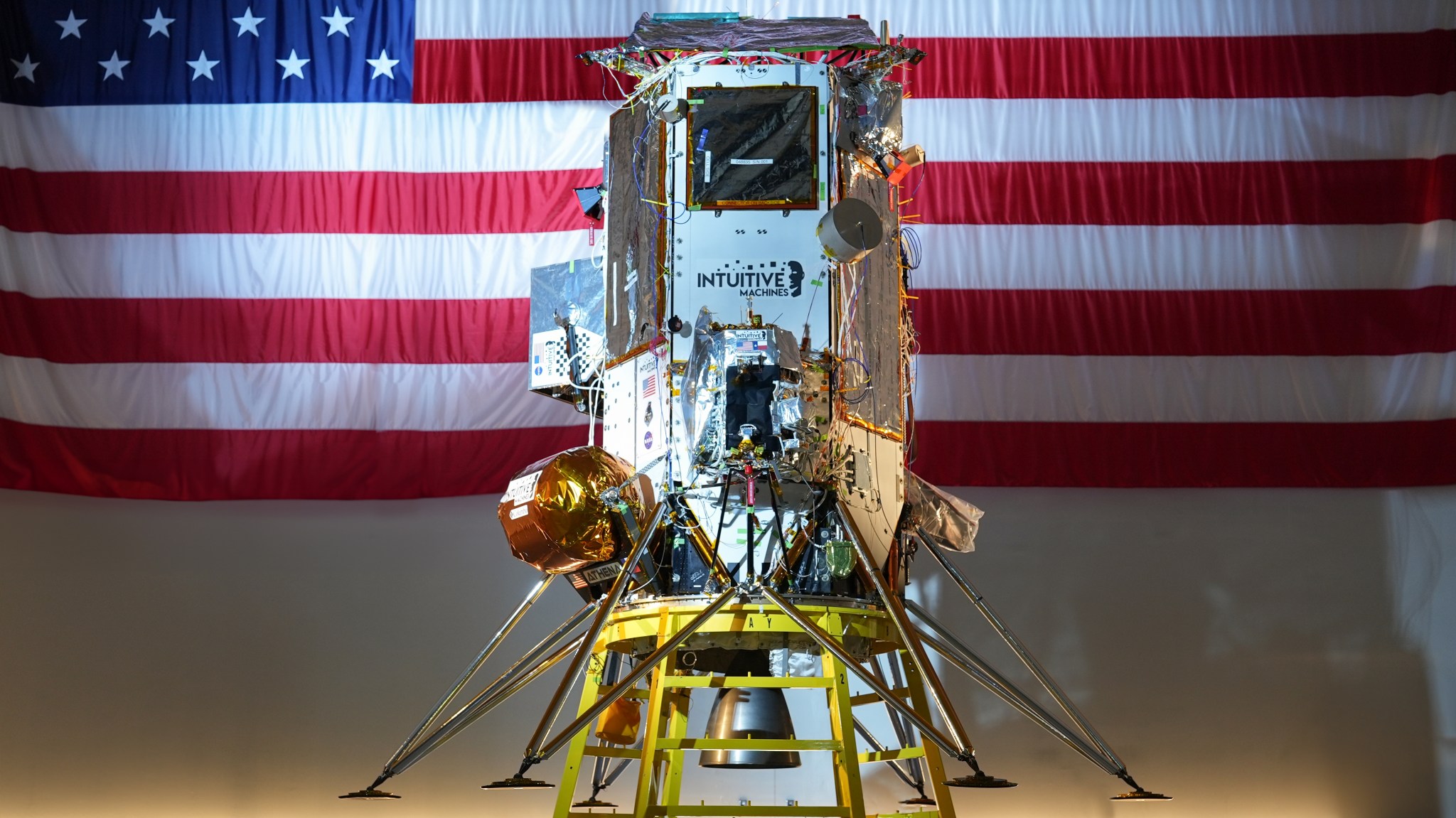
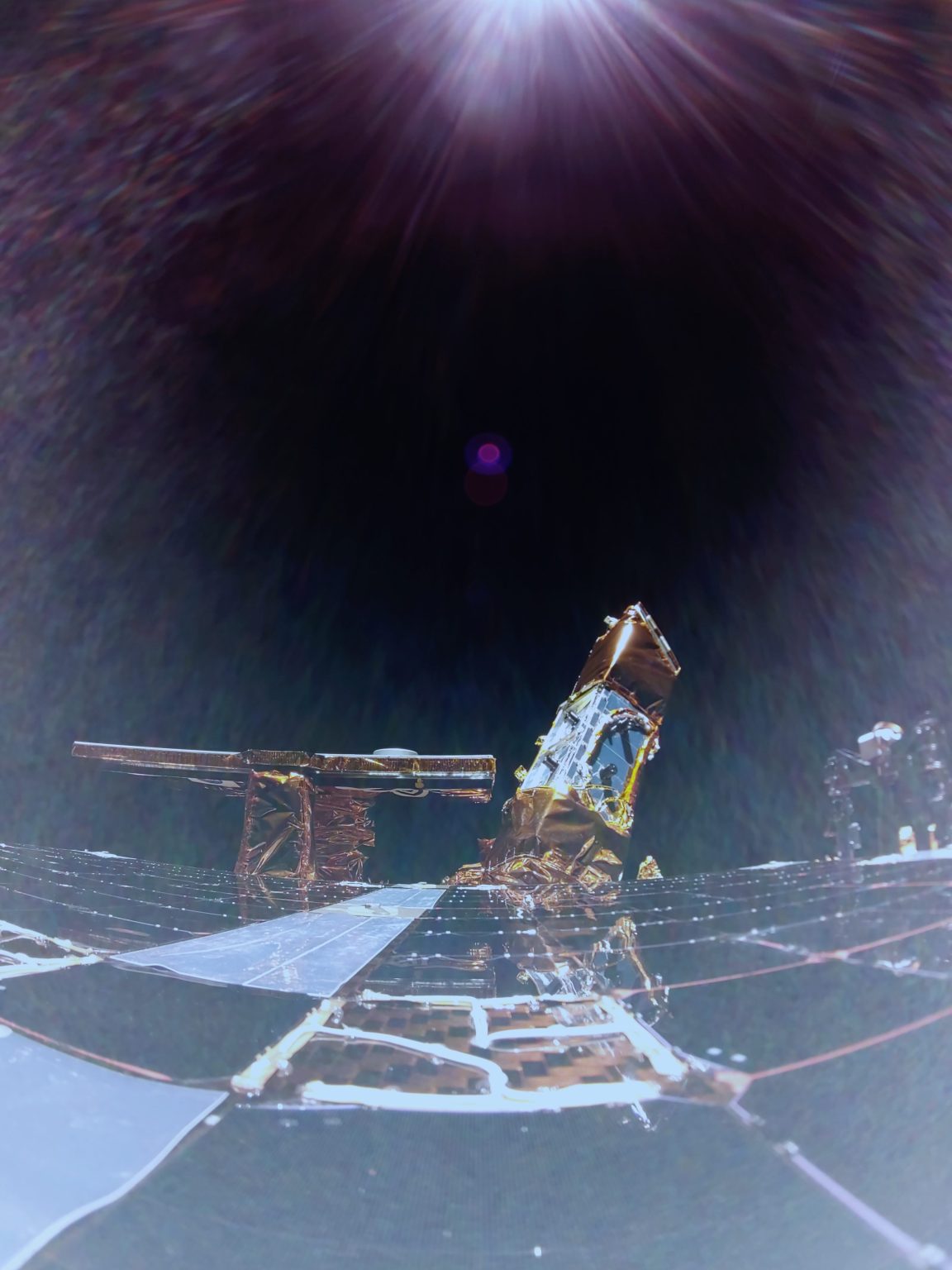
As NASA partners with American industry to deliver science and technology payloads to the Moon, a dedicated team behind the scenes ensures every mission is grounded in strategy, compliance, and innovation. Leading that effort is Aubrie Henspeter, who advises all aspects of procurement for NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative—one of the cornerstone projects supporting the Artemis campaign.
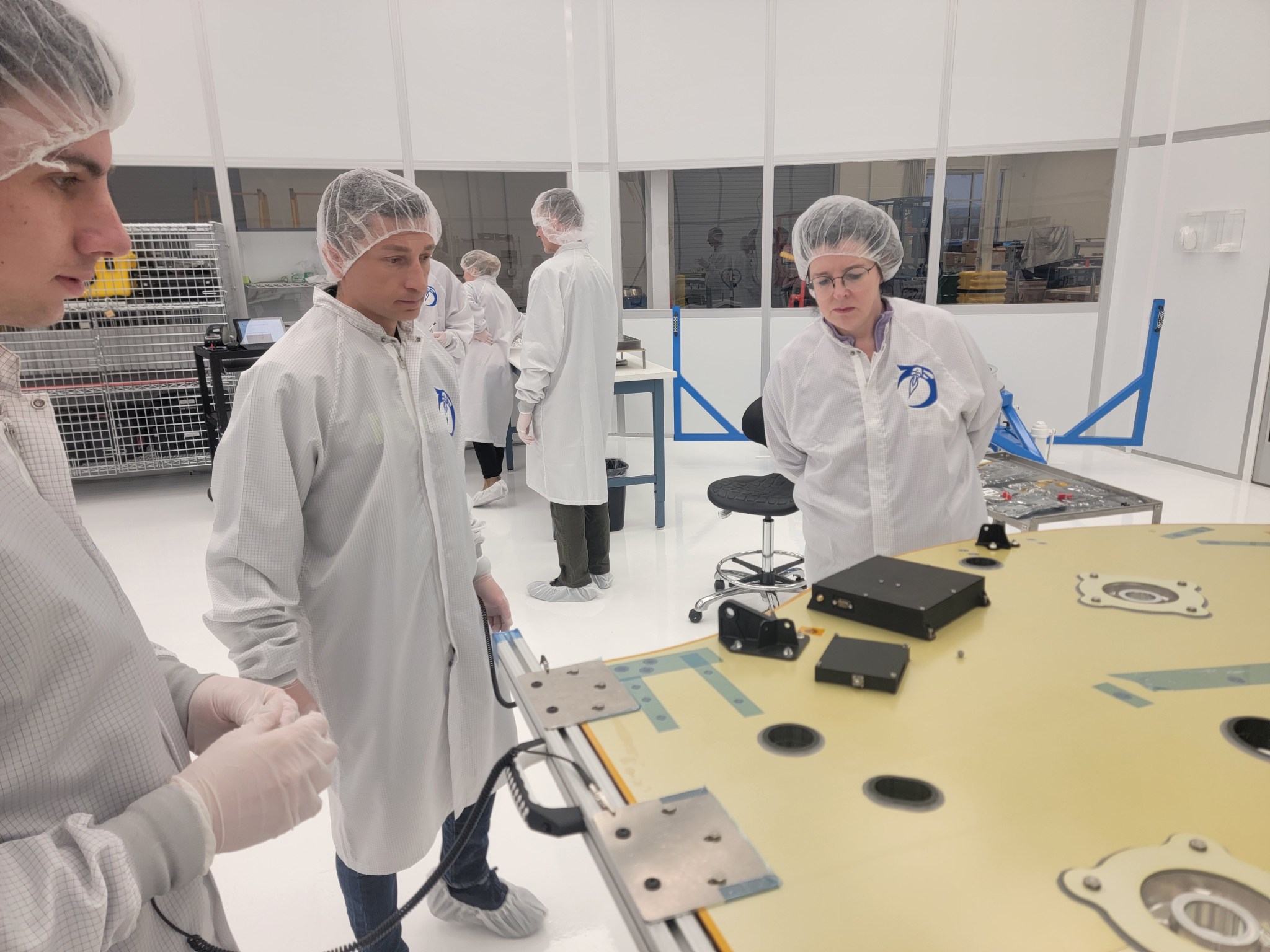
With 20 years at NASA, Henspeter brings multifaceted experience to her role as CLPS procurement team lead in the Lunar & Planetary Exploration Procurement Office at Johnson Space Center in Houston. Her job is equal parts problem-solving, mentoring, and strategizing—all focused on enabling commercial partners to deliver NASA payloads to the lunar surface faster, more affordably, and more efficient than ever before.
“It’s been a great experience to see the full lifecycle of a project—from soliciting requirements to launching to the Moon,” said Henspeter. “We work to continuously adjust as the lunar industry grows and improve procurement terms and conditions by incorporating lessons learned.”
Henspeter leads a team of six contracting officers and contract specialists, managing workload priorities and supporting the continuity of seven commercial missions currently on contract. She also helps shape upcoming contract opportunities for future lunar deliveries, constantly seeking creative procurement strategies within a commercial firm-fixed-price framework.
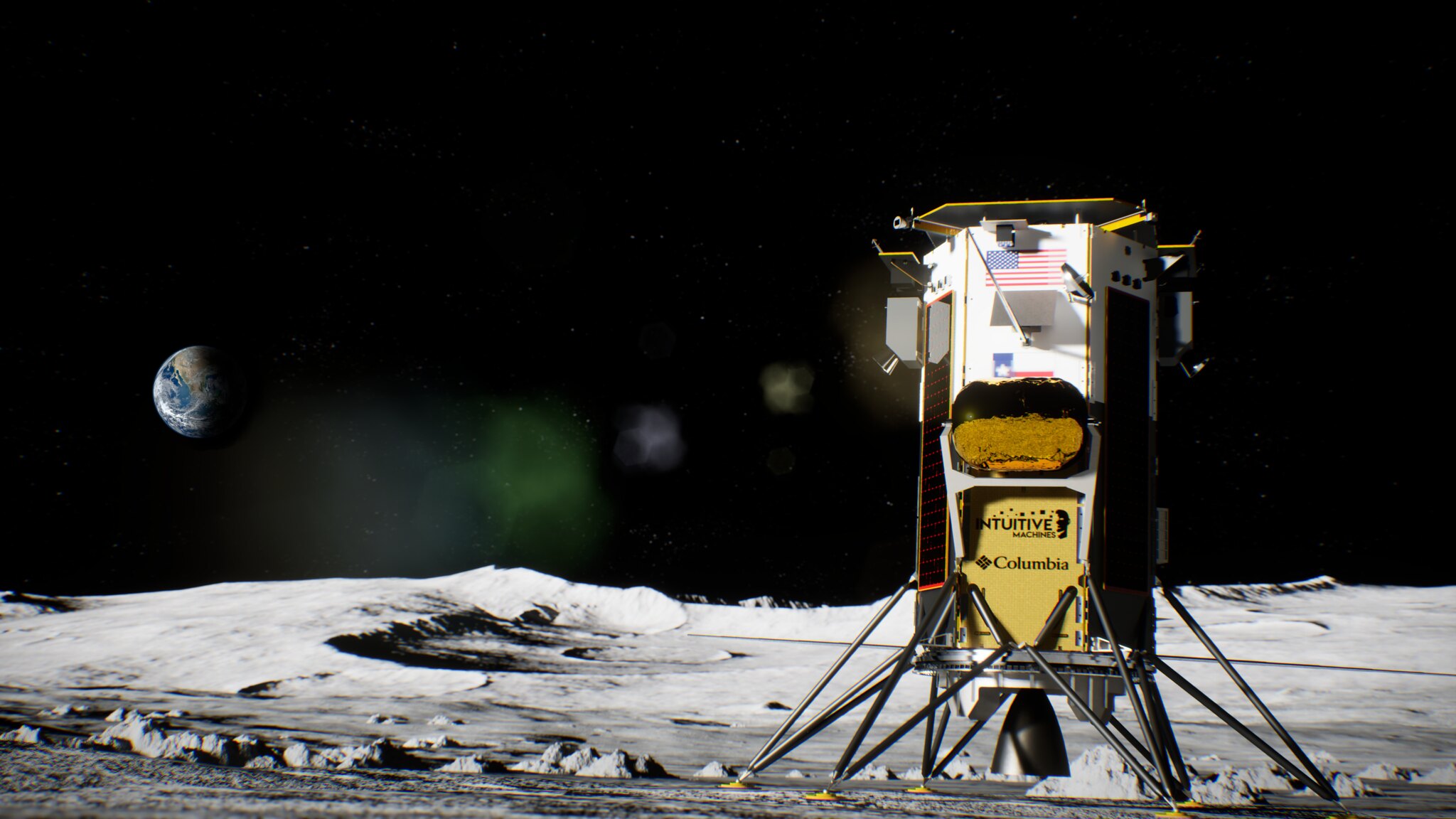
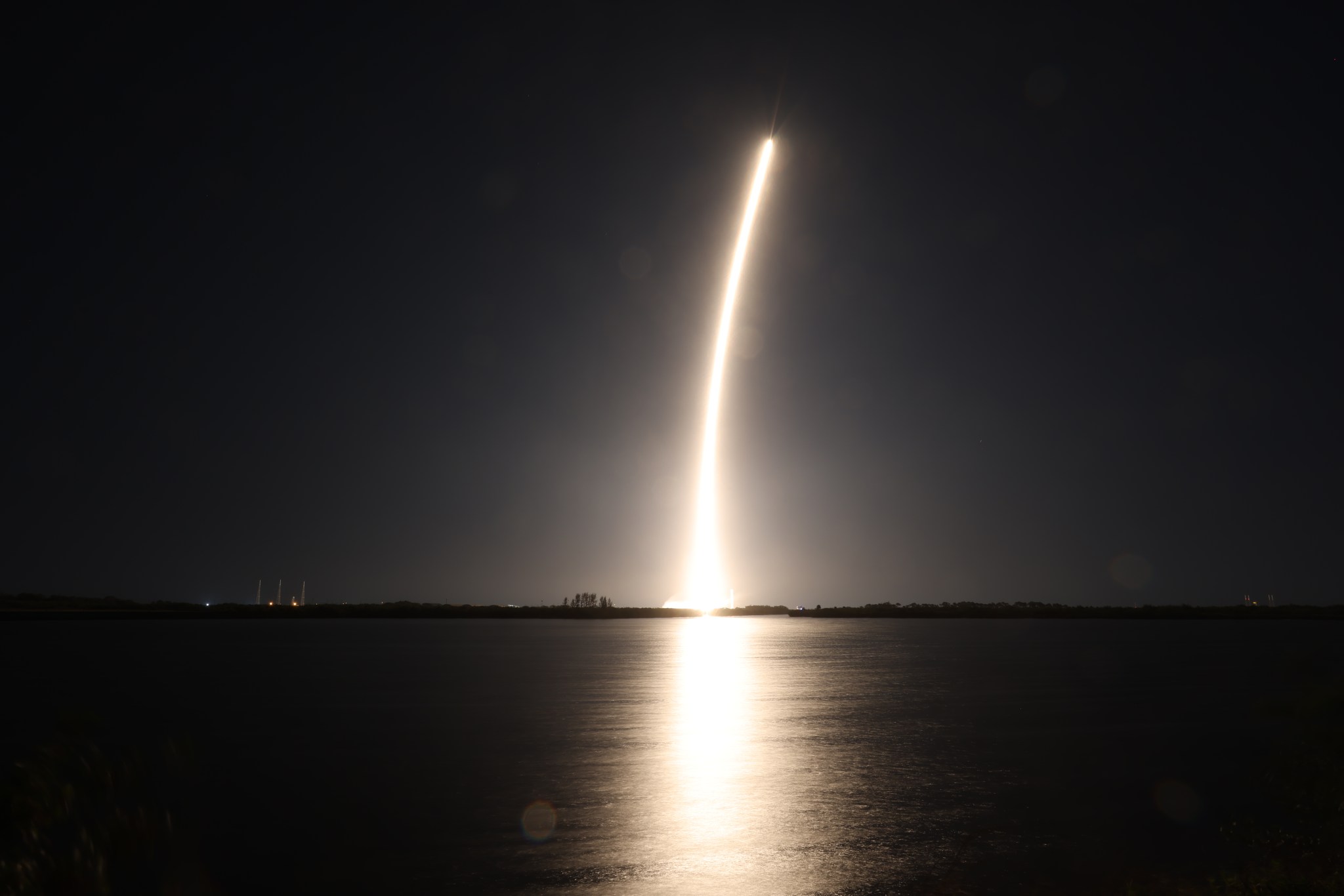
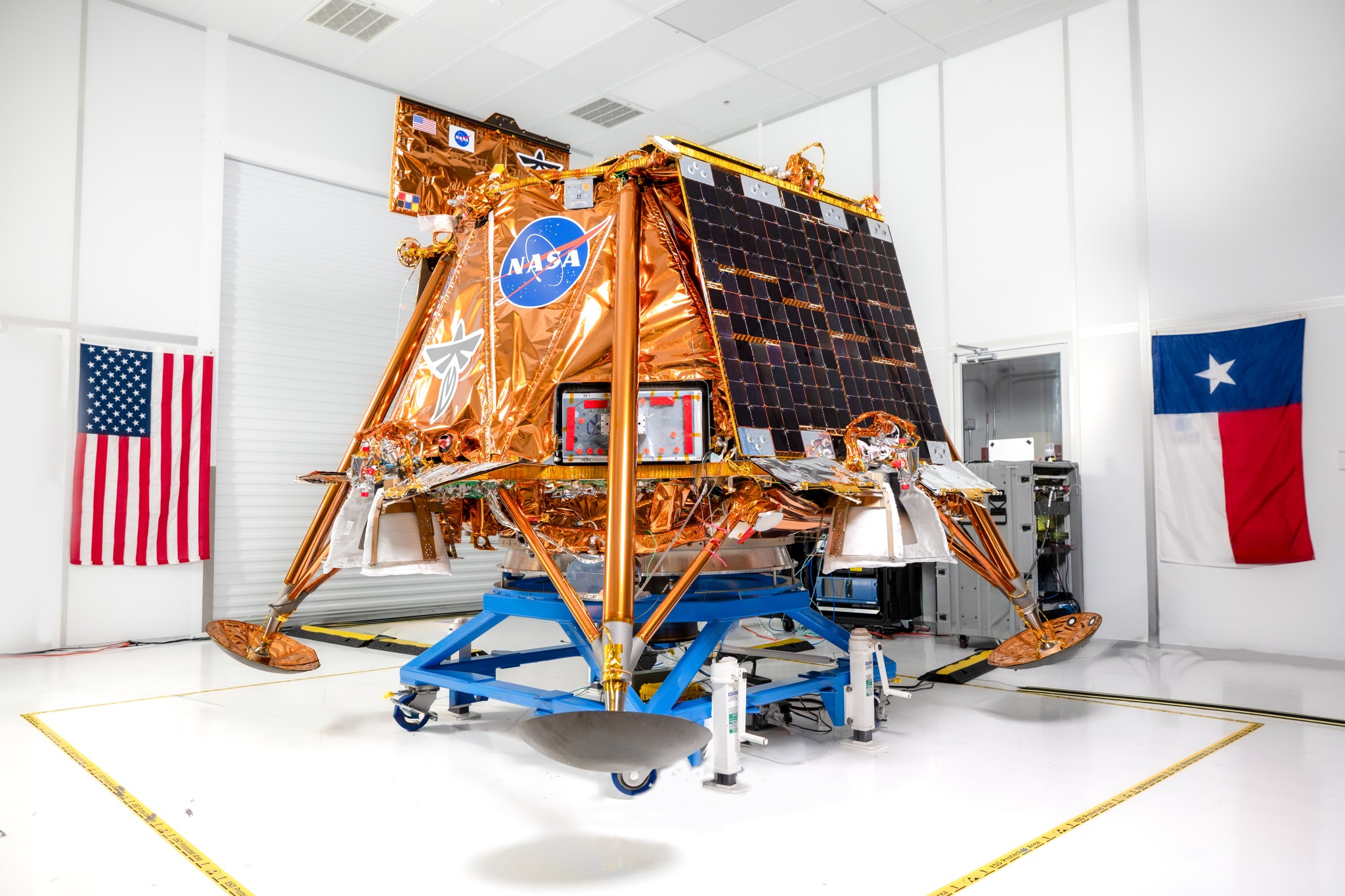
NASA launched the CLPS initiative in 2018 to create a faster, more flexible way to partner with commercial companies for lunar deliveries. Thirteen vendors are participating as part of a multi-award contract, each eligible to compete for individual task orders to deliver NASA science and technology payloads to the Moon. These deliveries support Artemis goals by enabling new discoveries, testing key technologies, and preparing for long-term human exploration on the lunar surface.
In May 2023, Henspeter received the NASA Exceptional Service Medal for her leadership on CLPS from 2018–2023. For her, the recognition reflects the team’s spirit and collaboration.
“I genuinely enjoy working on this project because of its lean, adaptable approach and the amazing team involved,” she said. “When all of us across NASA work together we are the most successful and can achieve our mission.”
That sense of collaboration and adaptability has shaped many of the insights Henspeter has gained throughout her career—lessons she now applies daily to help the team stay aligned and prepared.
One of those key lessons: always keep the contract current.
“It’s all good until it isn’t, and then everyone asks—what does the contract say?” she said. “Open communication and up-to-date documentation, no matter how minor the change, are essential.”
Over the course of her career, Henspeter has learned to prioritize preparation, adaptability, and strong working relationships.
“Preparation in procurement is conducting thorough market research, understanding the regulations, finding the gray areas, and developing a strategy that best meets the customer’s needs,” she said. “Adaptability means staying committed to the goal while remaining open and flexible on how to get there.”
That philosophy has helped her navigate everything from yearlong international contract negotiations with foreign partners to pivoting a customer from a sole-source request to a competitive procurement that ultimately saved costs and expanded opportunity.
“NASA is full of brilliant people, and it can be challenging to present alternatives. But through clear communication and data-driven recommendations, we find solutions that work,” Henspeter said.

As she looks to the Artemis Generation, Henspeter hopes to pass along a deep respect for teamwork and shared purpose.
“Every contribution matters. Whether it seems big or small, it makes a difference in achieving our mission,” she said. “I take pride in my role and in being part of the NASA team.”