Unearthly Plumbing Required for Plant Watering in Space
4 min read
Unearthly Plumbing Required for Plant Watering in Space
NASA is demonstrating new microgravity fluids technologies to enable advanced “no-moving-parts” plant-watering methods aboard spacecraft.
Crop production in microgravity will be important to provide whole food nutrition, dietary variety, and psychological benefits to astronauts exploring deep space. Unfortunately, even the simplest terrestrial plant watering methods face significant challenges when applied aboard spacecraft due to rogue bubbles, ingested gases, ejected droplets, and myriad unstable liquid jets, rivulets, and interface configurations that arise in microgravity environments.
In the weightlessness of space, bubbles do not rise, and droplets do not fall, resulting in a plethora of unearthly fluid flow challenges. To tackle such complex dynamics, NASA initiated a series of Plant Water Management (PWM) experiments to test capillary hydroponics aboard the International Space Station in 2021. The series of experiments continue to this day, opening the door not only to supporting our astronauts in space with the possibility of fresh vegetables, but also to address a host of challenges in space, such as liquid fuel management, Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC); and even urine collection.
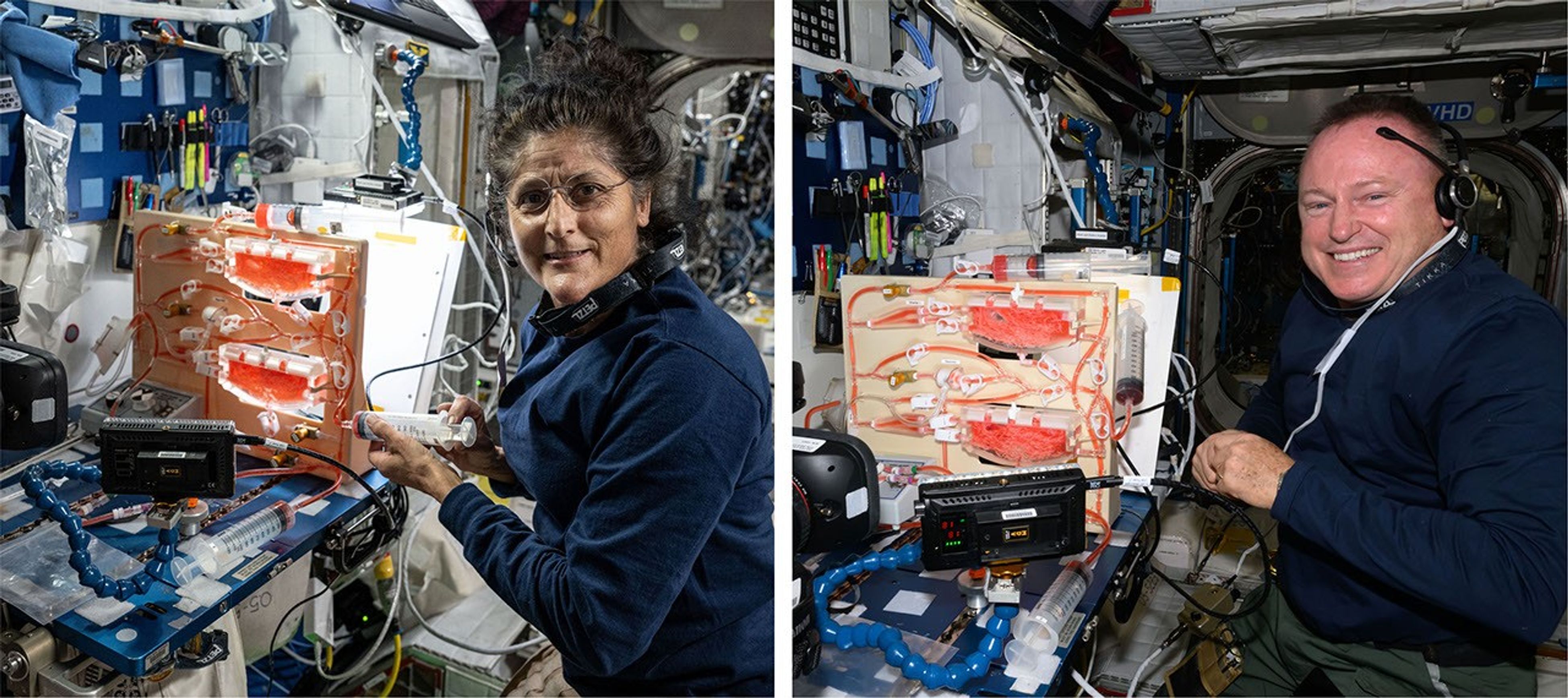
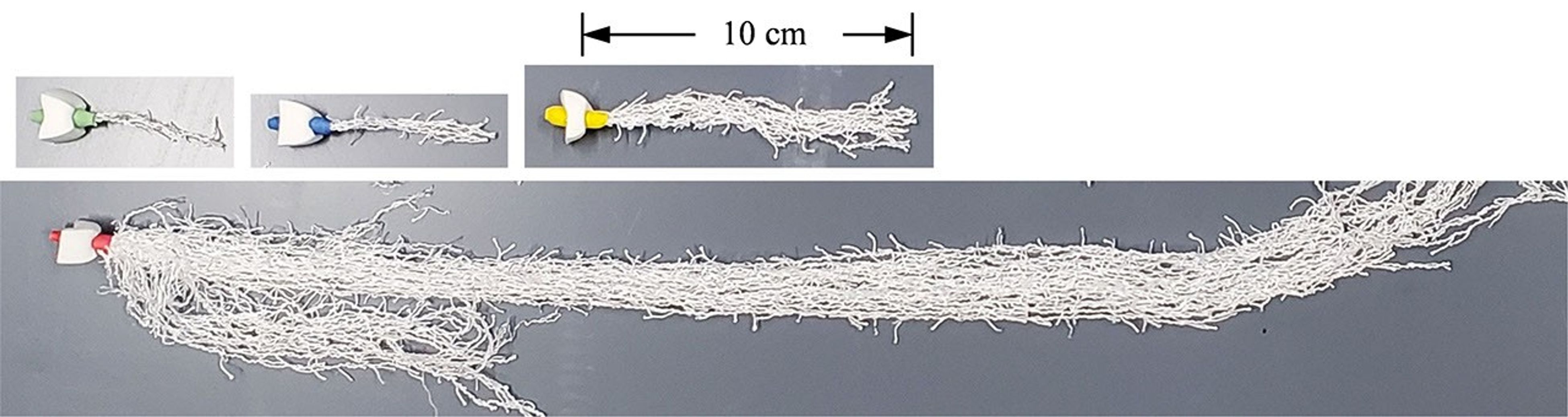
The latest PWM hardware (PWM-5 and -6) involves three test units, each consisting of a variable-speed pump, tubing harness, assorted valves and syringes, and either one serial or two parallel hydroponic channels. This latest setup enables a wider range of parameters to be tested—e.g., gas and liquid flow rates, fill levels, inlet/outlet configurations, new bubble separation methods, serial and parallel flows, and new plant root types, numbers, and orders.
Most of the PWM equipment shipped to the space station consists of 3-D printed, flight-certified materials. The crew assembles the various system configurations on a workbench in the open cabin of the station and then executes the experiments, including routine communication with the PWM research team on the ground. All the quantitative data is collected via a single high-definition video camera.
The PWM hardware and procedures are designed to incrementally test the system’s capabilities for hydroponic and ebb and flow, and to repeatedly demonstrate priming, draining, serial/parallel channel operation, passive bubble management, limits of operation, stability during perturbations, start-up, shut-down, and myriad clean plant-insertion, saturation, stable flow, and plant-removal steps.
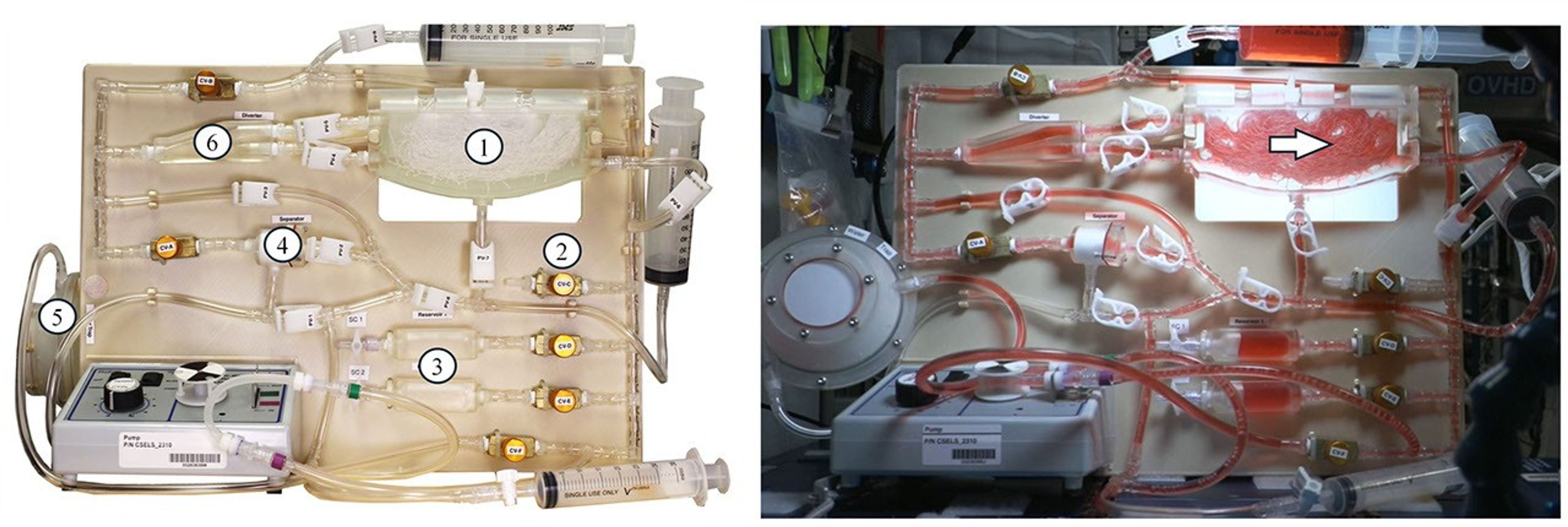
The recent results of the PWM-5 and -6 technology demonstrations aboard the space station have significantly advanced the technology used for passive plant watering in space. These quantitative demonstrations established hydroponic and ebb and flow watering processes as functions of serial and parallel channel fill levels, various types of engineered plant root models, and pump flow rates—including single-phase liquid flows and gas-liquid two-phase flows.
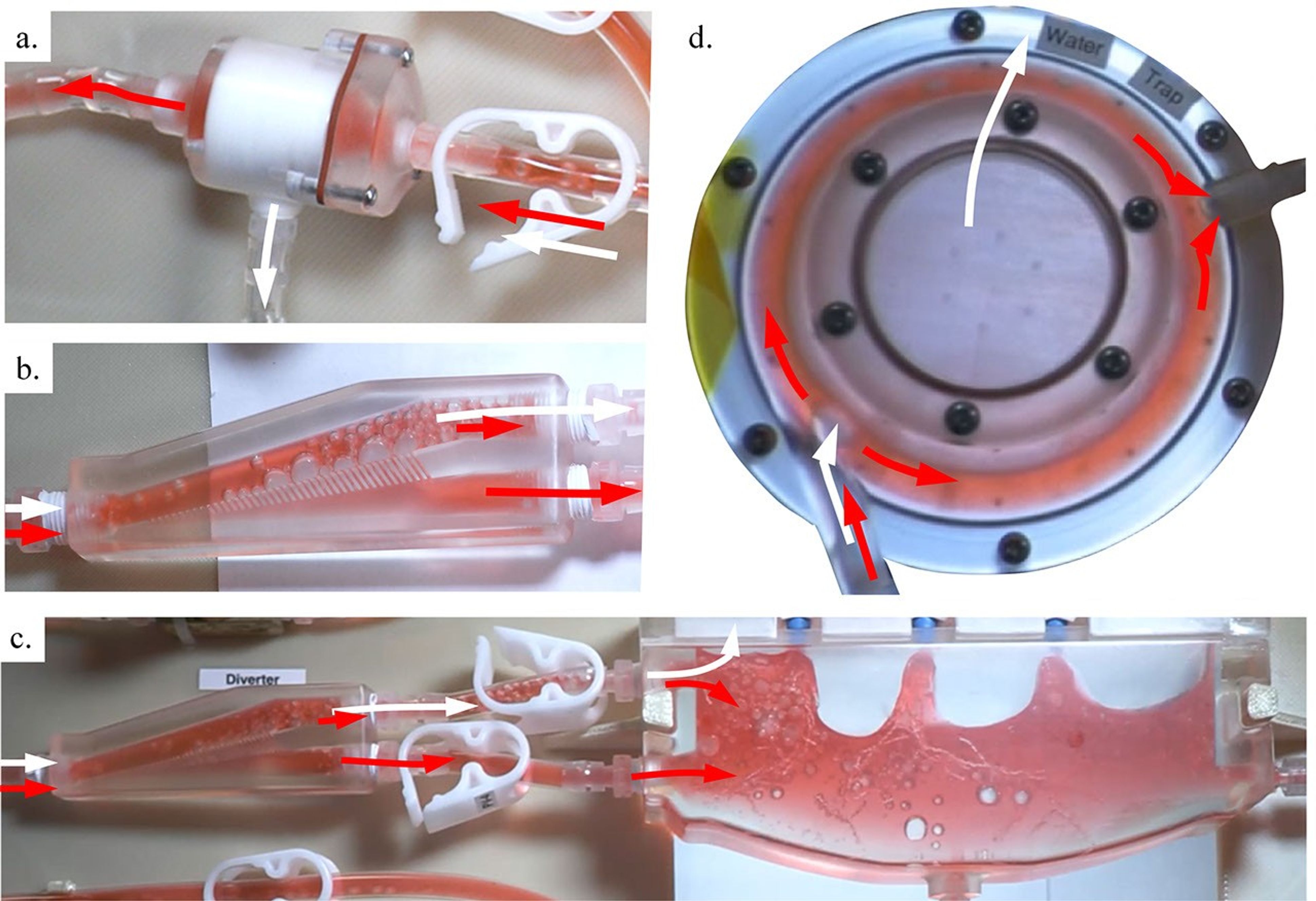
Critical PWM plumbing elements perform the role of passive gas-liquid separation (i.e., the elimination of bubbles from liquid and vice versa), which routinely occurs on Earth due to gravitational effects. The PWM-5 and -6 hardware in effect replaces the passive role of gravity with the passive roles of surface tension, wetting, and system geometry. In doing so, highly reliable “no-moving-parts” plumbing devices act to restore the illusive sense of up and down in space. For example,
- hundreds of thousands of oxygenating bubbles generated by a passive aerator are 100% separated by the PWM bubble separator providing single-phase liquid flow to the hydroponic channel,
- 100% of the inadvertent liquid carry-over is captured in the passive water trap, and
- all of the bubbles reaching the bubble diverter are directed to the upper inlet of the hydroponic channel where they are driven ever-upward by the channel geometry, confined by the first plant root, and coalesce leaving the liquid flow as a third, redundant, 100% passive phase-separating mechanism.
The demonstrated successes of PWM-5 and -6 offer a variety of ready plug-and-play solutions for effective plant watering in low- and variable-gravity environments, despite the challenging wetting properties of the water-based nutrient solutions used to water plants. Though a variety of root models are demonstrated by PWM-5 and -6, the remaining unknown is the role that real growing plants will play in such systems. Acquiring such knowledge may only be a matter of time.
Project Lead: Dr. Mark Weislogel, IRPI LLC
Sponsoring Organization: Biological and Physical Sciences Division