Ransomware Review December 2024: FunkSec’s Meteoric Rise and the Growing Threat of RaaS
Written by: Ekrem Çelik, Cybersecurity Researcher
Welcome to the December 2024 ransomware update, where we highlight the latest trends, threat actors, and developments in the ransomware ecosystem to keep CISOs and third-party risk managers informed and prepared.
The Black Kite Research & Intelligence Team (BRITE) tracked 535 ransomware incidents in December 2024. While it didn’t surpass the record-breaking 595 victims in November, December still proved to be a significant month. Of these incidents, an overwhelming 244 were in the United States and 27 in Canada, highlighting North America’s ongoing struggle as a primary target for ransomware attacks.
Top Threat Actors in December 2024
1. FunkSec Emerges as a Major Player with 87 Victims
December marked a turning point in the ransomware landscape as FunkSec dethroned RansomHub to become the leading threat actor with 87 victims. What makes FunkSec’s rise particularly remarkable is that it is a relatively new group in the ecosystem. Their operations have not been limited to ransomware; the group has been actively selling admin access and super access for various companies, offering a troubling range of services to their buyers. FunkSec primarily targeted the information sector and public administration industries this month, demonstrating a calculated focus on critical and data-heavy sectors. Their rapid ascent highlights their aggressive strategies and growing influence in the ransomware ecosystem.
2. RansomHub Maintains Stability with 57 Victims
After dominating the leaderboard since July, RansomHub dropped to the second spot with 57 victims in December. Despite losing its leadership position, RansomHub maintained its reputation as a consistent player in the ransomware space, continuing to target high-value organizations globally.
Akira Surges with 46 Victims
The Akira group surged to the third position this month with 46 victims, showcasing one of its most active and aggressive months of the year. Akira’s operations this month highlighted their ability to capitalize on vulnerabilities and expand their victim pool, signaling their intent to climb higher in the ransomware hierarchy.
They Hate Being Forgotten: Clop (Cl0p) Is Back Again
The Clop group added a chaotic twist to the month. Exploiting the CLEO vulnerability in December, they initially promised to release victim data “within 48 hours.” Then they postponed to December 30, only to announce they were “taking a holiday break” and would publish data after their return.

In total, Clop announced 66 victims, but BRITE believes the actual number is higher. Their erratic behavior has left many wondering if the group is losing its grip or simply playing for attention. Regardless, Clop’s actions remind us of the unpredictable nature of threat actors and the challenges of staying ahead of them.
One thing is clear: Clop, despite its chaotic actions, refuses to be forgotten and remains a noteworthy player in the ransomware ecosystem.
LockBit 4.0 Introduces RaaS Pricing Model for Just $777
LockBit, once the industry leader, seems to be struggling to reclaim its former prominence. December saw the launch of LockBit 4.0, a move that many interpreted as an attempt to stay relevant. Along with this update, the group introduced a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) pricing model for just $777, making their tools accessible to smaller players in the ecosystem.
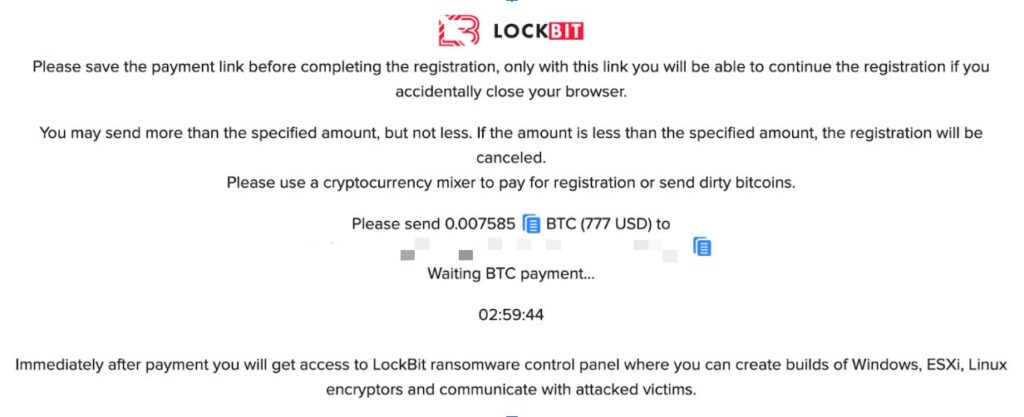
This shift has raised eyebrows across the cybersecurity world. Is it a sign of innovation or desperation? Many believe this move reflects LockBit’s declining influence after facing increased law enforcement pressure and internal challenges.
What stands out most is that LockBit’s struggles highlight a harsh reality: nothing in the ransomware world is unbreakable. Even the strongest groups can fall, showing how unpredictable and tough this space can be.
At the same time, their collapse shows how much it affects the whole ecosystem. It’s also a reminder of how hard it is to keep a group running steadily and stay on top in such a challenging environment.
RaaS Revolutionized Cybercrime in December 2024
The rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) has been one of the defining trends of December.
- LockBit’s pricing model set off a ripple effect, inspiring other groups like FunkSec to adopt similar strategies.
- Smaller threat actors are now able to access sophisticated ransomware tools at lower costs, democratizing cybercrime and complicating defense efforts.

RaaS not only increases the number of attacks but also lowers the barrier for entry, making it easier for less experienced actors to enter the game. This trend, if it continues, could make 2025 an even more challenging year for cybersecurity professionals.
2024: A Record-Breaking Year for Ransomware
2024 was a record-breaking year for ransomware. As groups continue to grow, tactics evolve, and victims are added to the lists, we can expect more records to be set in the coming months.
At Black Kite, the BRITE team remains committed to tracking threat actors in real time, analyzing their movements, and staying aware of emerging threats. As we enter 2025, staying one step ahead has never been more critical.For weekly updates on emerging cyber threats, please follow our Focus Friday blog series and LinkedIn account.
Learn more about the rising ransomware attacks in the full 2025 Healthcare Ransomware Report — accessible instantly, no download required.
The post Ransomware Review December 2024: FunkSec’s Meteoric Rise and the Growing Threat of RaaS appeared first on Black Kite.