xAI Dev Leaks API Key for Private SpaceX, Tesla LLMs
An employee at Elon Musk’s artificial intelligence company xAI leaked a private key on GitHub that for the past two months could have allowed anyone to query private xAI large language models (LLMs) which appear to have been custom made for working with internal data from Musk’s companies, including SpaceX, Tesla and Twitter/X, KrebsOnSecurity has learned.

Image: Shutterstock, @sdx15.
Philippe Caturegli, “chief hacking officer” at the security consultancy Seralys, was the first to publicize the leak of credentials for an x.ai application programming interface (API) exposed in the GitHub code repository of a technical staff member at xAI.
Caturegli’s post on LinkedIn caught the attention of researchers at GitGuardian, a company that specializes in detecting and remediating exposed secrets in public and proprietary environments. GitGuardian’s systems constantly scan GitHub and other code repositories for exposed API keys, and fire off automated alerts to affected users.
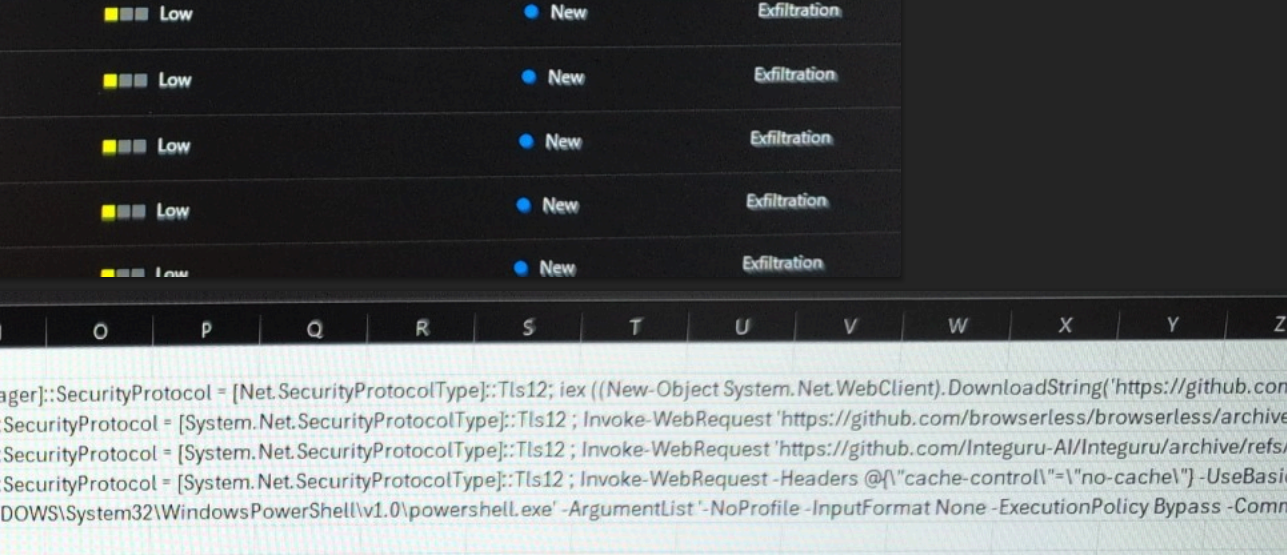
GitGuardian’s Eric Fourrier told KrebsOnSecurity the exposed API key had access to several unreleased models of Grok, the AI chatbot developed by xAI. In total, GitGuardian found the key had access to at least 60 fine-tuned and private LLMs.
“The credentials can be used to access the X.ai API with the identity of the user,” GitGuardian wrote in an email explaining their findings to xAI. “The associated account not only has access to public Grok models (grok-2-1212, etc) but also to what appears to be unreleased (grok-2.5V), development (research-grok-2p5v-1018), and private models (tweet-rejector, grok-spacex-2024-11-04).”
Fourrier found GitGuardian had alerted the xAI employee about the exposed API key nearly two months ago — on March 2. But as of April 30, when GitGuardian directly alerted xAI’s security team to the exposure, the key was still valid and usable. xAI told GitGuardian to report the matter through its bug bounty program at HackerOne, but just a few hours later the repository containing the API key was removed from GitHub.
“It looks like some of these internal LLMs were fine-tuned on SpaceX data, and some were fine-tuned with Tesla data,” Fourrier said. “I definitely don’t think a Grok model that’s fine-tuned on SpaceX data is intended to be exposed publicly.”
xAI did not respond to a request for comment. Nor did the 28-year-old xAI technical staff member whose key was exposed.
Carole Winqwist, chief marketing officer at GitGuardian, said giving potentially hostile users free access to private LLMs is a recipe for disaster.
“If you’re an attacker and you have direct access to the model and the back end interface for things like Grok, it’s definitely something you can use for further attacking,” she said. “An attacker could it use for prompt injection, to tweak the (LLM) model to serve their purposes, or try to implant code into the supply chain.”
The inadvertent exposure of internal LLMs for xAI comes as Musk’s so-called Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) has been feeding sensitive government records into artificial intelligence tools. In February, The Washington Post reported DOGE officials were feeding data from across the Education Department into AI tools to probe the agency’s programs and spending.
The Post said DOGE plans to replicate this process across many departments and agencies, accessing the back-end software at different parts of the government and then using AI technology to extract and sift through information about spending on employees and programs.
“Feeding sensitive data into AI software puts it into the possession of a system’s operator, increasing the chances it will be leaked or swept up in cyberattacks,” Post reporters wrote.
Wired reported in March that DOGE has deployed a proprietary chatbot called GSAi to 1,500 federal workers at the General Services Administration, part of an effort to automate tasks previously done by humans as DOGE continues its purge of the federal workforce.
A Reuters report last month said Trump administration officials told some U.S. government employees that DOGE is using AI to surveil at least one federal agency’s communications for hostility to President Trump and his agenda. Reuters wrote that the DOGE team has heavily deployed Musk’s Grok AI chatbot as part of their work slashing the federal government, although Reuters said it could not establish exactly how Grok was being used.
Caturegli said while there is no indication that federal government or user data could be accessed through the exposed x.ai API key, these private models are likely trained on proprietary data and may unintentionally expose details related to internal development efforts at xAI, Twitter, or SpaceX.
“The fact that this key was publicly exposed for two months and granted access to internal models is concerning,” Caturegli said. “This kind of long-lived credential exposure highlights weak key management and insufficient internal monitoring, raising questions about safeguards around developer access and broader operational security.”