Focus Friday: Addressing Third-Party Risks in PAN-OS, Ivanti Connect Secure, Zimbra, and Cacti Vulnerabilities
Written by: Ferdi Gül
In this week’s Focus Friday, we examine high-impact vulnerabilities affecting Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS, Ivanti Connect Secure, Zimbra Collaboration, and Cacti, all of which pose significant third-party risk concerns. These vulnerabilities range from remote code execution (RCE) flaws to SQL injection attacks that could lead to data breaches, system takeovers, and supply chain risks.
Organizations relying on network security appliances, email collaboration tools, and monitoring frameworks must take proactive measures to assess their exposure and secure their vendor ecosystem against these threats. In this blog, we provide an in-depth Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective, detailing how these vulnerabilities could impact vendor security postures and what questions security teams should ask to mitigate risks.
Additionally, we highlight how Black Kite’s FocusTags™ provide real-time insights into vendor exposure, helping organizations prioritize remediation efforts and streamline their risk management processes.

CVE-2025-0108, CVE-2025-0110: Authentication Bypass & Command Injection in PAN-OS
What are the PAN-OS Authentication Bypass and Command Injection Vulnerabilities?
Two high-severity vulnerabilities have been identified in Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS, affecting network security devices:
- CVE-2025-0108 (Authentication Bypass – CVSS: 8.8):
This vulnerability affects the management web interface of PAN-OS. An unauthenticated attacker with network access can bypass authentication and invoke specific PHP scripts. While it does not allow remote code execution, it compromises system integrity and confidentiality. - CVE-2025-0110 (Command Injection – CVSS: 8.6):
Found in the OpenConfig plugin, this vulnerability enables an authenticated administrator with gNMI request privileges to inject and execute arbitrary commands. The commands run as the _openconfig user, which has Device Administrator privileges, potentially leading to full system compromise.
Both vulnerabilities were published on February 12, 2025. One proof-of-concept exploit is available on github.com. There is no evidence of active exploitation or inclusion in CISA’s KEV catalog at this time. However, PAN-OS vulnerabilities have been targeted in the past, making proactive mitigation crucial.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Be Concerned About These Vulnerabilities?
Third-party risk management (TPRM) professionals should be concerned due to the critical role of PAN-OS in enterprise cybersecurity.
- Authentication Bypass (CVE-2025-0108):
Attackers could exploit this flaw to gain unauthorized access to PAN-OS management functions, leading to potential misconfigurations, unauthorized changes, or exposure of sensitive network settings. - Command Injection (CVE-2025-0110):
If the OpenConfig plugin is enabled, an attacker with administrator access could execute arbitrary system commands, escalating privileges or deploying persistent malware on PAN-OS devices.
For vendors relying on PAN-OS for perimeter security, exploitation of these vulnerabilities could lead to network-wide security breaches, data exposure, and compromised firewall configurations.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors?
To assess vendor exposure, TPRM professionals should ask:
- Have you identified any PAN-OS devices in your environment that are running vulnerable versions (before PAN-OS 11.2.4-h4, 11.1.6-h1, 10.2.13-h3, 10.1.14-h9)?
- Do you use the OpenConfig plugin in PAN-OS? If so, have you verified that it is updated to version 2.1.2 or later?
- What access controls are in place to restrict exposure of the PAN-OS management web interface to untrusted networks?
- Have you applied Palo Alto Networks’ recommended mitigations, such as disabling unused plugins and restricting management access?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to this Risk
To mitigate the risk associated with these vulnerabilities, vendors should:
✔ Upgrade PAN-OS to patched versions:
- PAN-OS 11.2 → Upgrade to 11.2.4-h4 or later
- PAN-OS 11.1 → Upgrade to 11.1.6-h1 or later
- PAN-OS 10.2 → Upgrade to 10.2.13-h3 or later
- PAN-OS 10.1 → Upgrade to 10.1.14-h9 or later
- If running PAN-OS 11.0 (EoL), upgrade to a supported version.
✔ Update OpenConfig plugin to version 2.1.2 or later (if enabled).
✔ Restrict management interface access to trusted internal IPs only.
✔ Disable the OpenConfig plugin if not in use to reduce the attack surface.
✔ Monitor system logs for unusual access or command execution activity.
✔ Apply Palo Alto Networks’ Threat Prevention rules to block potential exploits (Threat IDs 510000, 510001).
How TPRM Professionals Can Leverage Black Kite for These Vulnerabilities
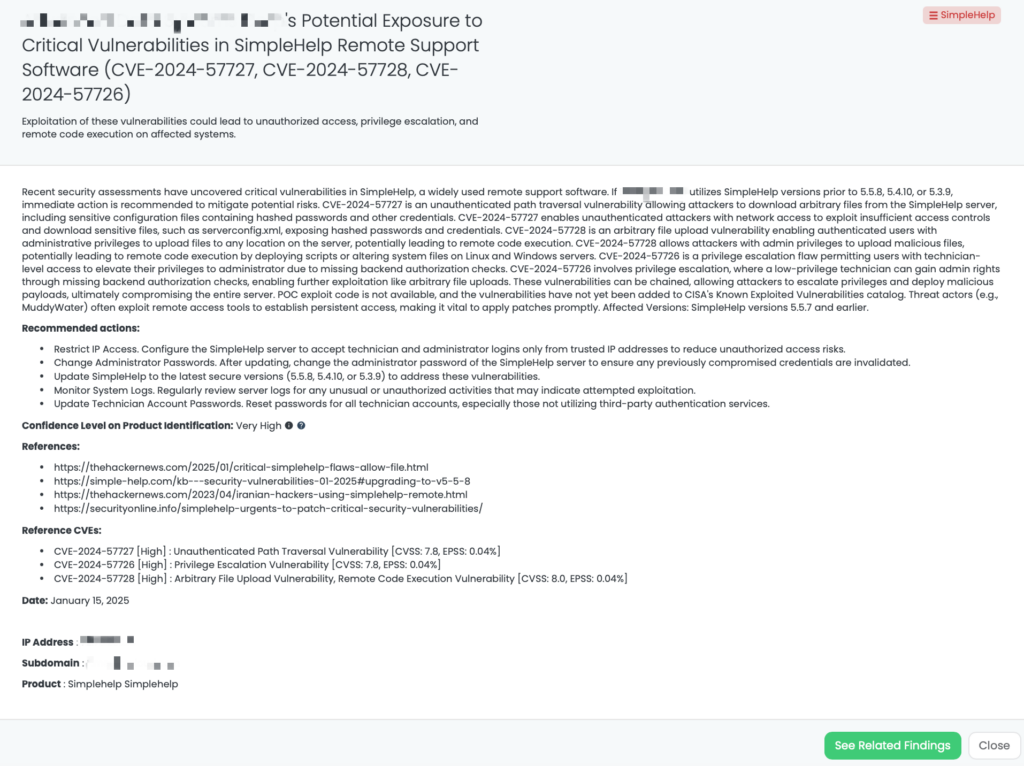
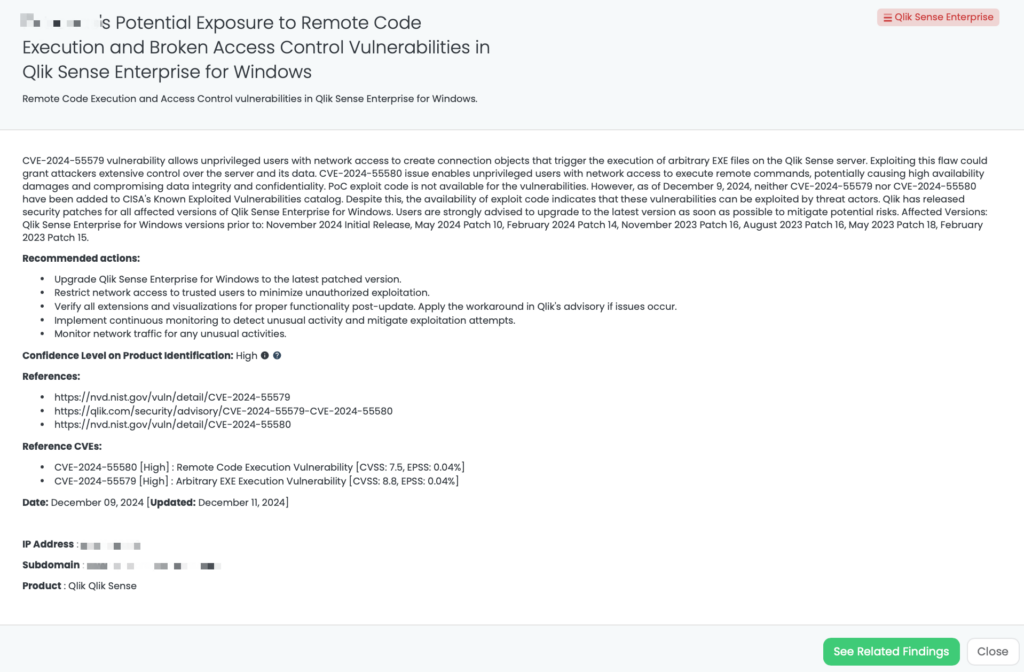
Black Kite has tagged this issue as “PAN-OS – Feb2025” with a VERY HIGH confidence level.
- The FocusTag™ identifies vendors potentially affected by CVE-2025-0108 and CVE-2025-0110.
- Black Kite provides asset intelligence, including IP addresses and subdomains hosting vulnerable PAN-OS instances.
The FocusTag™ was published on February 13, 2025, allowing TPRM teams to take proactive measures before potential exploitation.
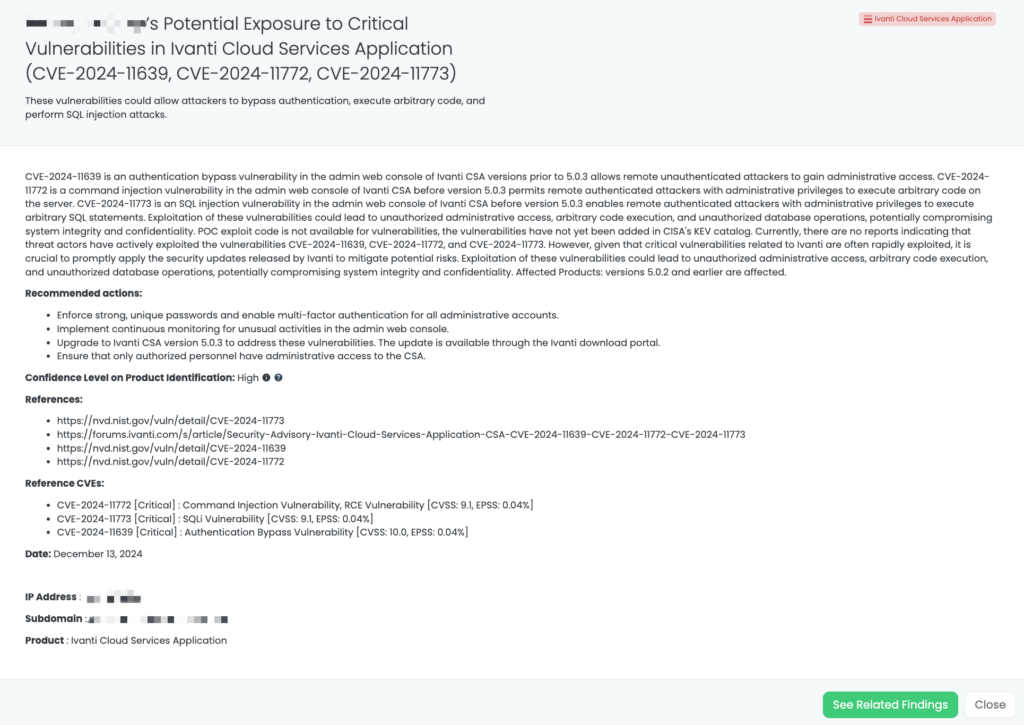
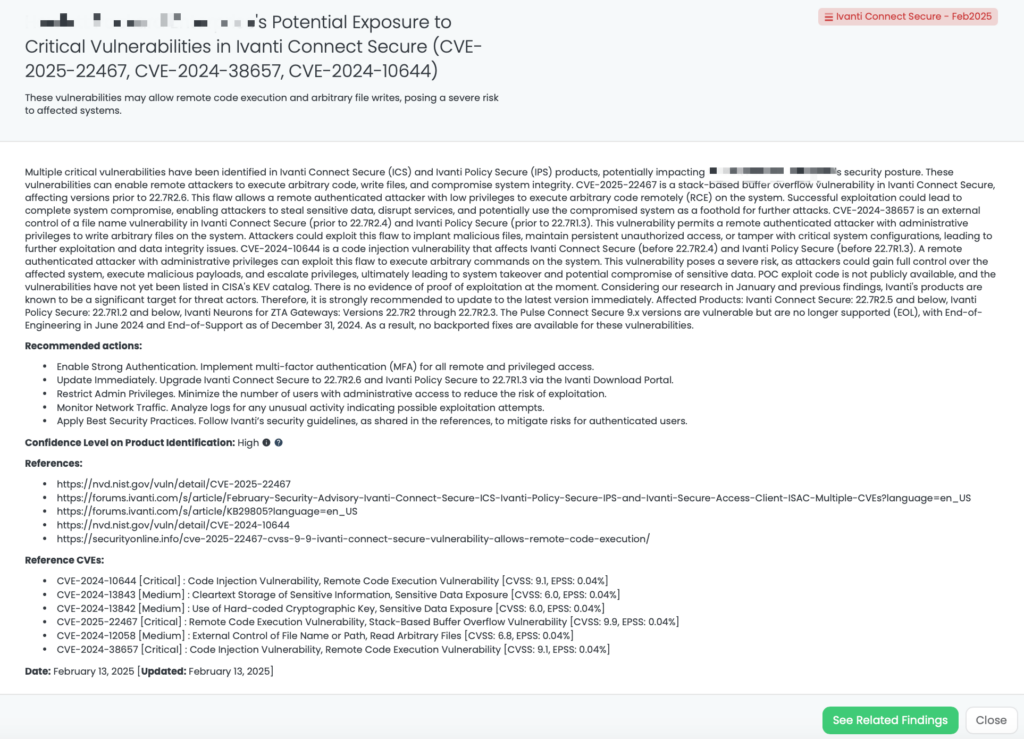
CVE-2025-22467, CVE-2024-38657, CVE-2024-10644: Critical Vulnerabilities in Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure
What Are the Critical Vulnerabilities in Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure?
Multiple critical vulnerabilities have been identified in Ivanti Connect Secure (ICS) and Ivanti Policy Secure (IPS) products:
- CVE-2025-22467 (CVSS: 9.9): A stack-based buffer overflow vulnerability in ICS versions prior to 22.7R2.6. This flaw allows a remote authenticated attacker with low privileges to execute arbitrary code, potentially leading to full system compromise.
- CVE-2024-38657 (CVSS: 9.1): An external control of file name or path vulnerability affecting ICS (before 22.7R2.4) and IPS (before 22.7R1.3). A remote authenticated attacker with administrative privileges can write arbitrary files on the system, which may lead to unauthorized file manipulation or system compromise.
- CVE-2024-10644 (CVSS: 9.1): A code injection vulnerability in ICS (before 22.7R2.4) and IPS (before 22.7R1.3). This allows a remote authenticated attacker with administrative privileges to execute arbitrary commands on the system, potentially resulting in complete system control.
These vulnerabilities were publicly disclosed on February 11, 2025. As of now, there is no evidence of active exploitation in the wild, and they have not been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. Other vulnerabilities to be mindful of include CVE-2024-12058 (arbitrary file read), CVE-2024-13842 (sensitive data exposure), and CVE-2024-13843 (cleartext storage of sensitive information), which, despite their lower CVSS scores, should still be carefully considered.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Be Concerned About These Vulnerabilities?
Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) professionals should be concerned due to the following reasons:
- Remote Code Execution Risks: Exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow attackers to execute arbitrary code or commands, leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential lateral movement within the network.
- Privilege Escalation: Attackers with low-level access could exploit these flaws to escalate privileges, gaining administrative control over critical systems.
- Supply Chain Impact: Vendors utilizing vulnerable versions of ICS and IPS may inadvertently expose connected organizations to security risks, emphasizing the importance of assessing third-party security postures.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors About These Vulnerabilities?
To assess vendor exposure, TPRM professionals should inquire:
- Which versions of Ivanti Connect Secure and Ivanti Policy Secure are currently deployed within your environment?
- Have the identified vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-22467, CVE-2024-38657, CVE-2024-10644) been remediated by updating to the latest recommended versions?
- What measures are in place to monitor and detect potential exploitation attempts related to these vulnerabilities?
- Is multi-factor authentication (MFA) enabled for all administrative access to these systems?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
To mitigate the risks associated with these vulnerabilities, vendors should:
✔ Update to Patched Versions:
- For Ivanti Connect Secure, upgrade to version 22.7R2.6 or later.
- For Ivanti Policy Secure, upgrade to version 22.7R1.3 or later.
✔ Restrict Administrative Privileges:
- Limit administrative access to essential personnel.
- Enforce principle of least privilege to reduce risk.
✔ Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
- Ensure MFA is enabled for all administrative and remote access.
✔ Monitor System Logs:
- Regularly review logs for unusual activities or signs of attempted exploitation.
✔ Apply Security Best Practices:
- Follow Ivanti’s security guidelines to mitigate risks associated with authenticated users.
How TPRM Professionals Can Leverage Black Kite for These Vulnerabilities
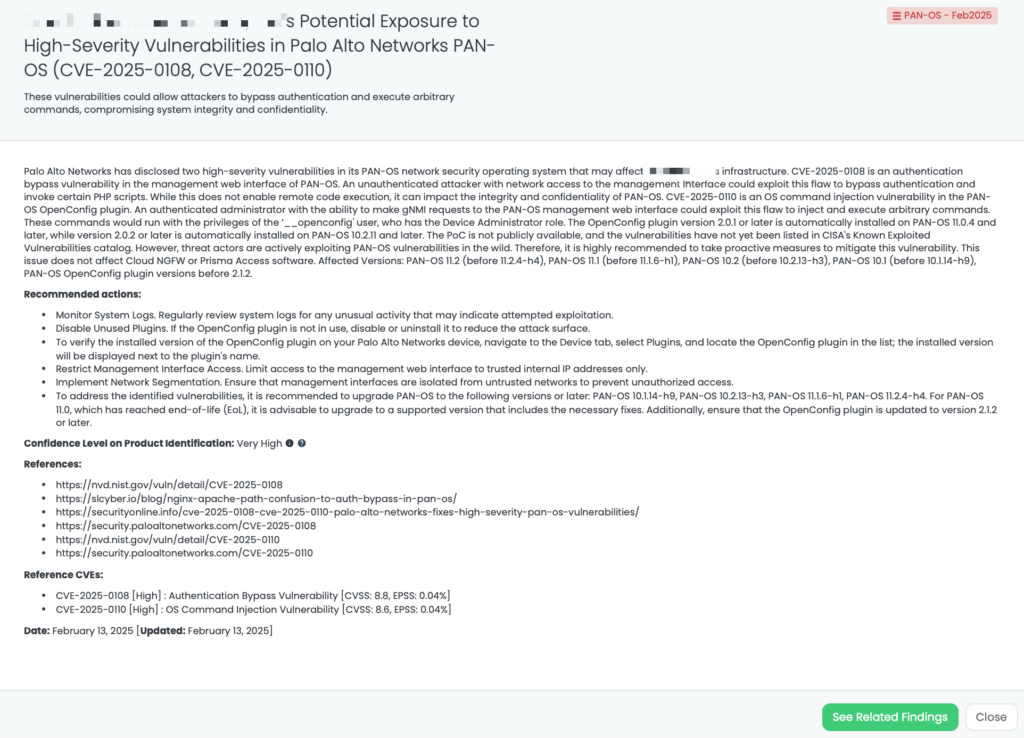
Black Kite has tagged these vulnerabilities under “Ivanti Connect Secure – Feb2025” with a HIGH confidence level.
- The FocusTag™ provides detailed information on vendors potentially affected by these vulnerabilities.
- Black Kite’s asset intelligence helps identify IP addresses and subdomains hosting vulnerable instances.
- This enables TPRM teams to proactively assess and address risks associated with these vulnerabilities.
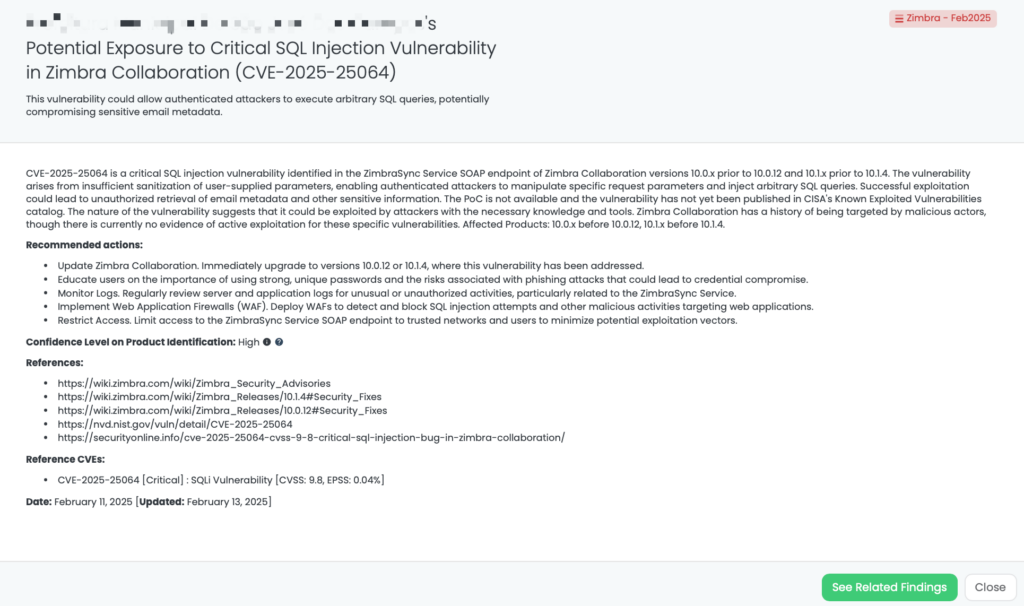
CVE-2025-25064: Zimbra Collaboration SQL Injection Vulnerability
Zimbra Collaboration (formerly known as Zimbra Collaboration Suite or ZCS) is an open-source and commercial groupware email platform. It includes features such as email, calendaring, contacts, task management, instant messaging, and file sharing, designed for enterprises, government institutions, and service providers.
What is CVE-2025-25064?
CVE-2025-25064 is a critical SQL injection vulnerability affecting Zimbra Collaboration versions 10.0.x prior to 10.0.12 and 10.1.x prior to 10.1.4. This flaw arises from insufficient sanitization of user-supplied parameters in the ZimbraSync Service SOAP endpoint. Authenticated attackers can exploit this vulnerability by manipulating specific request parameters to inject arbitrary SQL queries, potentially allowing unauthorized retrieval of email metadata and other sensitive information. The vulnerability has a CVSS score of 9.8, indicating its critical severity, and an EPSS score of 0.05%. It was publicly disclosed on February 9, 2025. As of now, there is no evidence of active exploitation in the wild, and it has not been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Be Concerned About CVE-2025-25064?
Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) professionals should be concerned about CVE-2025-25064 due to its potential impact on email security. Zimbra Collaboration is widely used by organizations for email and collaboration services. Exploitation of this vulnerability could allow attackers to access sensitive email metadata, leading to unauthorized disclosure of confidential information. If a vendor utilizes vulnerable Zimbra Collaboration products, their compromised systems could serve as entry points for attackers, resulting in data breaches and disruptions that may affect connected organizations.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors Regarding CVE-2025-25064?
To assess and mitigate risks associated with this vulnerability, TPRM professionals should inquire:
- Have you updated all instances of Zimbra Collaboration to versions 10.0.12 or 10.1.4, where CVE-2025-25064 has been patched?
- Can you confirm if you have implemented access restrictions to the ZimbraSync Service SOAP endpoint to trusted networks and users as recommended?
- Have you deployed Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) to detect and block SQL injection attempts targeting Zimbra Collaboration?
- Do you regularly monitor server and application logs for unusual or unauthorized activities, particularly related to the ZimbraSync Service?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors
Vendors using affected Zimbra Collaboration products should:
- Update Software: Upgrade to Zimbra Collaboration versions 10.0.12 or 10.1.4, where this vulnerability has been addressed.
- Restrict Access: Limit access to the ZimbraSync Service SOAP endpoint to trusted networks and users to minimize potential exploitation vectors.
- Implement Web Application Firewalls (WAF): Deploy WAFs to detect and block SQL injection attempts and other malicious activities targeting web applications.
- Monitor Logs: Regularly review server and application logs for unusual or unauthorized activities, particularly related to the ZimbraSync Service.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability?
Black Kite has proactively addressed this issue by publishing the “Zimbra – Feb2025” FocusTag™ on February 11, 2025. This tag enables TPRM professionals to identify vendors potentially affected by CVE-2025-25064. By providing detailed asset information, including IP addresses and subdomains associated with the compromised devices, Black Kite empowers organizations to assess and mitigate risks efficiently. This actionable intelligence allows for targeted inquiries and remediation efforts, ensuring a robust third-party risk management strategy.
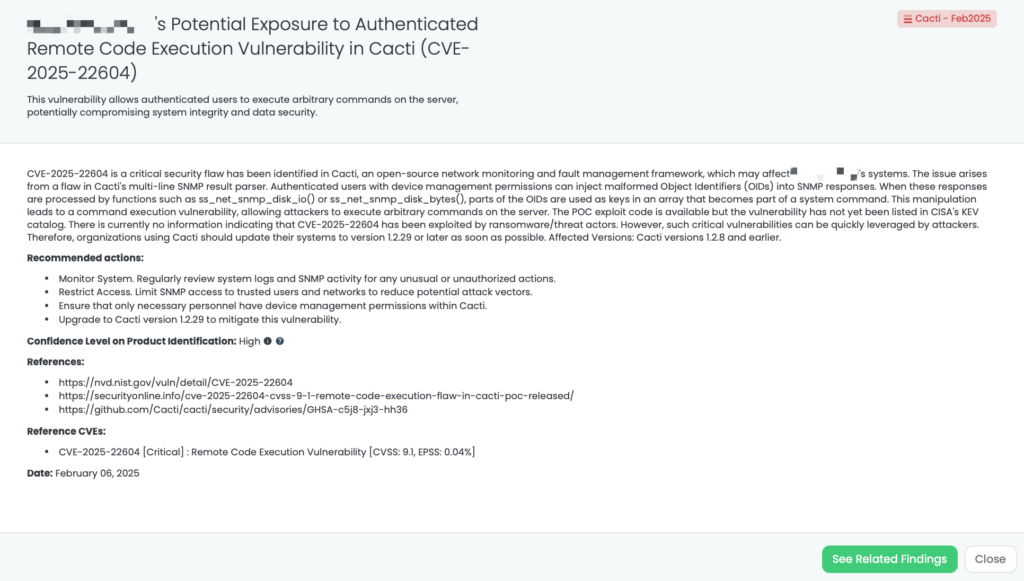
CVE-2025-22604: Critical Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Cacti
Cacti is an open-source network monitoring and graphing tool designed to collect, store, and visualize performance data for IT infrastructure. It is widely used by network administrators and IT professionals to monitor network devices, servers, and applications in real time.
What is the Cacti Remote Code Execution Vulnerability?
CVE-2025-22604 is a critical security flaw in Cacti, an open-source network monitoring and fault management framework. This vulnerability allows authenticated users with device management permissions to execute arbitrary commands on the server by injecting malformed Object Identifiers (OIDs) into SNMP responses. When processed by functions like ss_net_snmp_disk_io() or ss_net_snmp_disk_bytes(), parts of these OIDs are used as keys in an array that becomes part of a system command, leading to remote code execution (RCE). The vulnerability has a CVSS score of 9.1. It was publicly disclosed on January 26, 2025. There is no evidence of proof of exploitation at the moment.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Be Concerned About This Vulnerability?
Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) professionals should be concerned about CVE-2025-22604 because Cacti is widely used by organizations to monitor network performance and availability. A successful exploit of this vulnerability could allow attackers to execute arbitrary commands on the server, potentially compromising system integrity and data security. This could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information, disruption of network monitoring capabilities, and further exploitation within the organization’s network. Given the critical nature of this vulnerability and the availability of proof-of-concept exploit code, it is imperative for organizations to assess their exposure and ensure that their vendors have addressed this issue.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors About CVE-2025-22604?
To assess the risk associated with this vulnerability, TPRM professionals should consider asking vendors the following questions:
- Have you identified any instances of Cacti within your infrastructure that are affected by CVE-2025-22604?
- If so, have you updated all affected Cacti installations to version 1.2.29 or later to mitigate this vulnerability?
- What measures have you implemented to restrict SNMP access to trusted users and networks?
- Do you regularly monitor system logs and SNMP activity for unusual or unauthorized actions?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
Vendors should take the following actions to remediate the risk associated with CVE-2025-22604:
- Upgrade Cacti: Update all Cacti installations to version 1.2.29 or later, as this version addresses the vulnerability.
- Restrict SNMP Access: Limit SNMP access to trusted users and networks to reduce potential attack vectors.
- Monitor Systems: Regularly review system logs and SNMP activity for any unusual or unauthorized actions.
- Review Permissions: Ensure that only necessary personnel have device management permissions within Cacti.
How TPRM Professionals Can Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability
Black Kite has published a FocusTag™ titled “Cacti – Feb2025” to help organizations identify potential exposure to CVE-2025-22604. TPRM professionals can utilize this tag to assess their vendors’ risk related to this vulnerability. By leveraging Black Kite’s platform, professionals can identify vendors using vulnerable versions of Cacti and take proactive steps to mitigate potential risks. This includes obtaining asset information such as IP addresses and subdomains associated with the vendors’ systems, which is crucial for effective risk assessment and management.
Maximizing TPRM Effectiveness with Black Kite’s FocusTags™
With high-profile vulnerabilities such as PAN-OS authentication bypass (CVE-2025-0108), Ivanti Connect Secure RCE (CVE-2025-22467), Zimbra SQL injection (CVE-2025-25064), and Cacti remote code execution (CVE-2025-22604), organizations must rapidly assess third-party security risks to prevent cascading impacts. Black Kite’s FocusTags™ enable security teams to efficiently identify, analyze, and mitigate these threats by offering:
✅ Real-Time Risk Identification – Instant visibility into which vendors are affected by the latest vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take immediate action.
✅ Risk Prioritization – Insights into vendor importance and vulnerability severity, helping security teams allocate resources effectively.
✅ Informed Vendor Engagement – Targeted discussions with vendors about their security measures and remediation strategies for identified vulnerabilities.
✅ Comprehensive Security Posture Enhancement – A holistic view of third-party risks, enabling organizations to make data-driven security decisions.
By leveraging Black Kite’s FocusTags™, organizations can stay ahead of evolving cyber threats, ensuring proactive risk mitigation in their third-party ecosystems. These tags provide critical intelligence, transforming complex vulnerability data into actionable insights for better vendor security management.
Want to take a closer look at FocusTags™?
Take our platform for a test drive and request a demo today.
About Focus Friday
Every week, we delve into the realms of critical vulnerabilities and their implications from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. This series is dedicated to shedding light on pressing cybersecurity threats, offering in-depth analyses, and providing actionable insights.
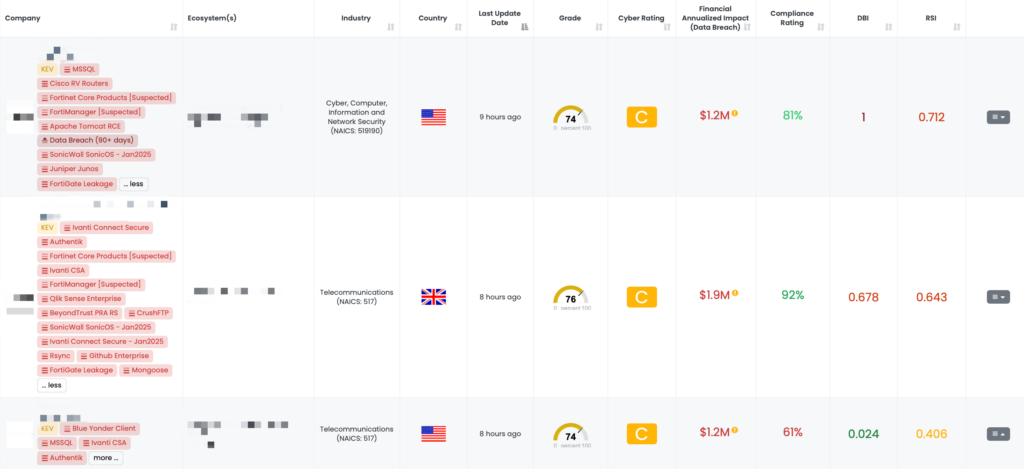
FocusTagsTM in the Last 30 Days:
- PAN-OS – Feb2025: CVE-2025-0108, CVE-2025-0110, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability, OS Command Injection Vulnerability in Palo Alto’s PAN-OS.
- Ivanti Connect Secure – Feb2025: CVE-2025-22467, CVE-2024-38657, CVE-2024-10644, Stack-Based Buffer Overflow Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, Code Injection Vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure & Policy Secure.
- Zimbra – Feb2025: CVE-2025-25064, SQLi Vulnerability in Zimbra Collaboration.
- Cacti – Feb2025: CVE-2025-22604, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Cacti.
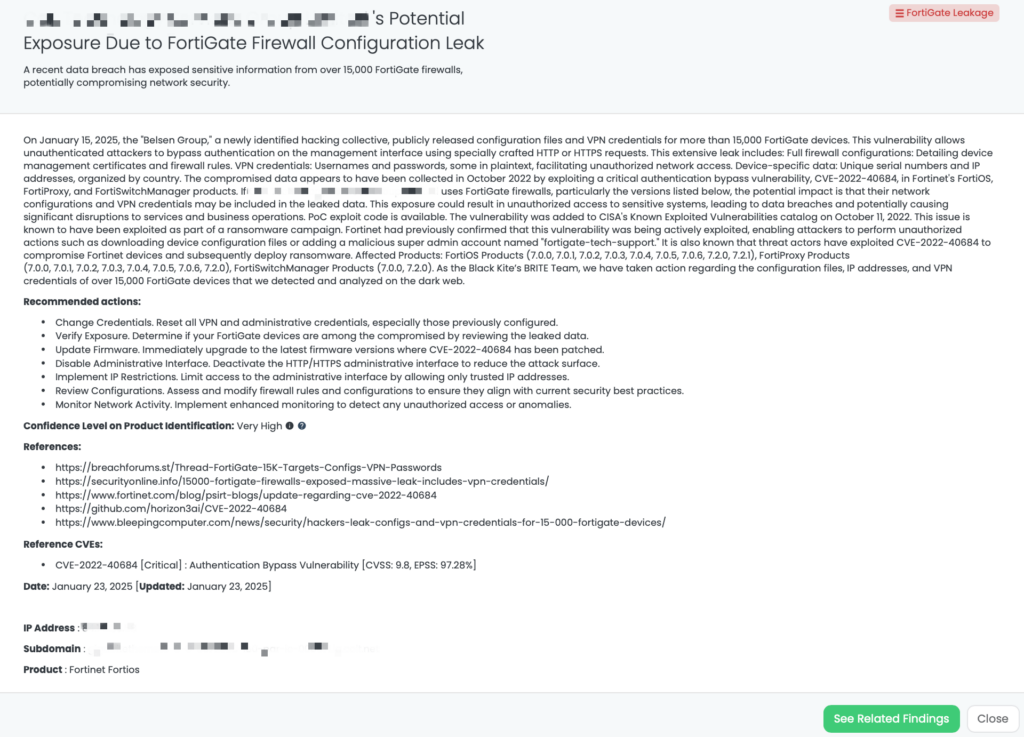
- FortiGate Leakage: CVE-2022-40684, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability, Leaked Configurations and VPN Credentials for 15,000 FortiGate Devices.
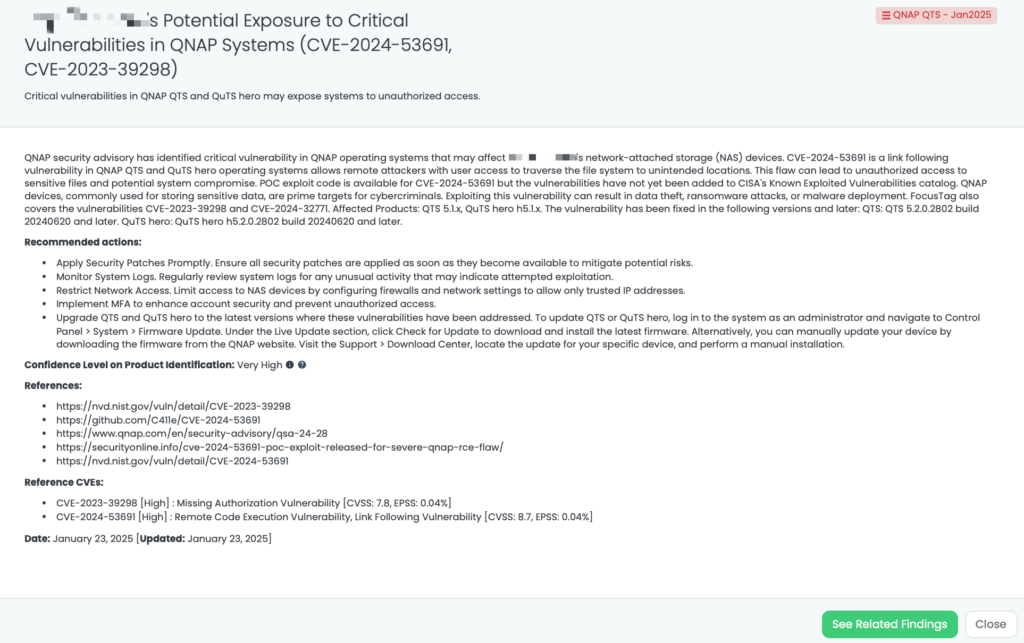
- QNAP QTS – Jan2025: CVE-2024-53691, CVE-2023-39298, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, Link Following Vulnerability, Missing Authorization Vulnerability in QNAP QTS.
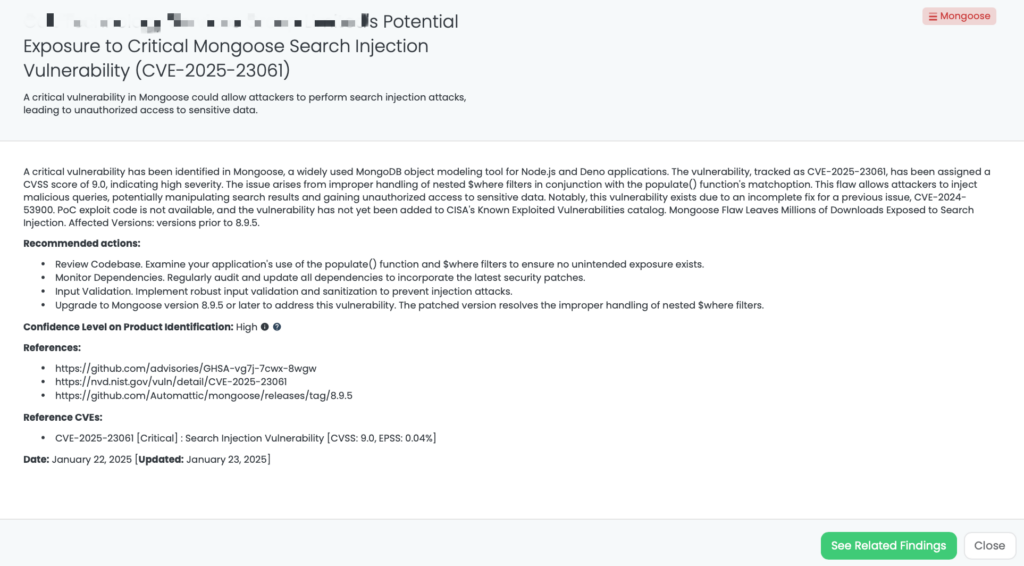
- Mongoose: CVE-2025-23061, Search Injection Vulnerability in Mongoose.
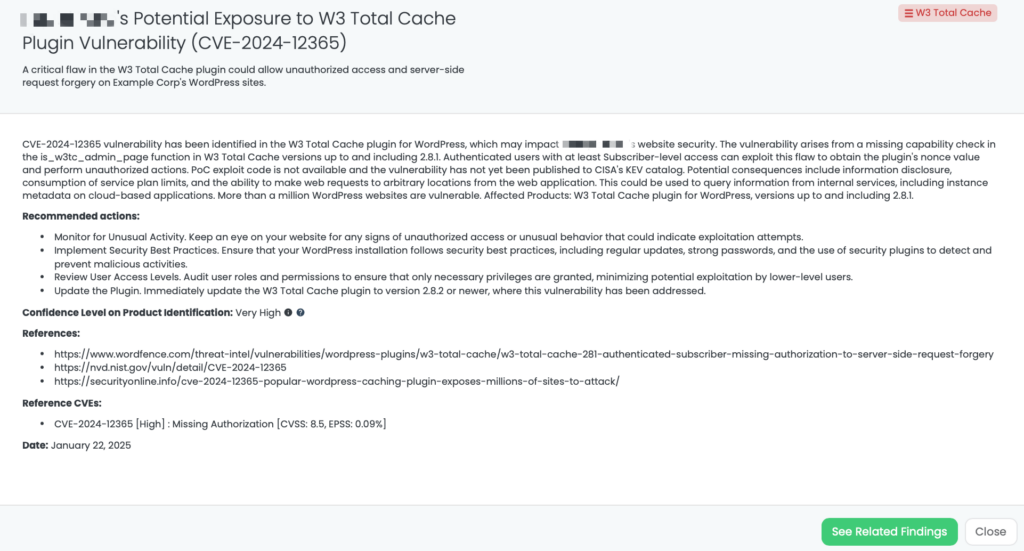
- W3 Total Cache: CVE-2024-12365, Missing Authorization Vulnerability in WordPress’ W3 Total Cache Plugin.
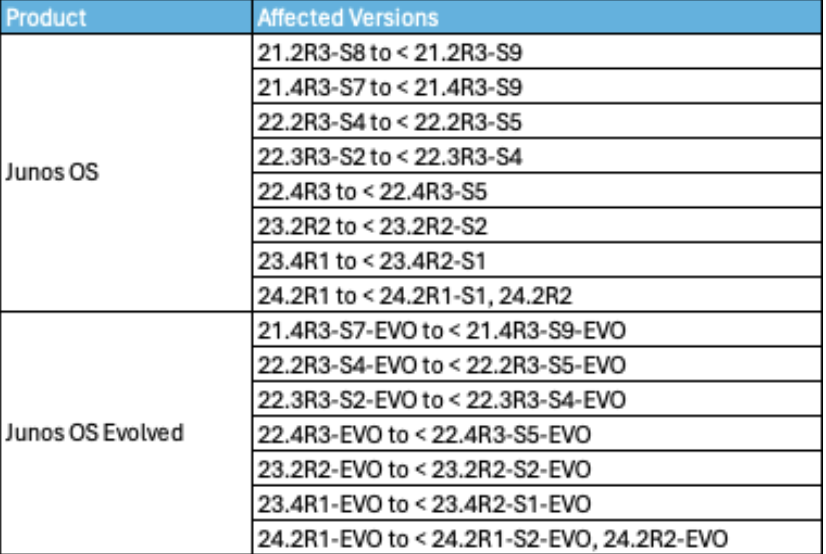
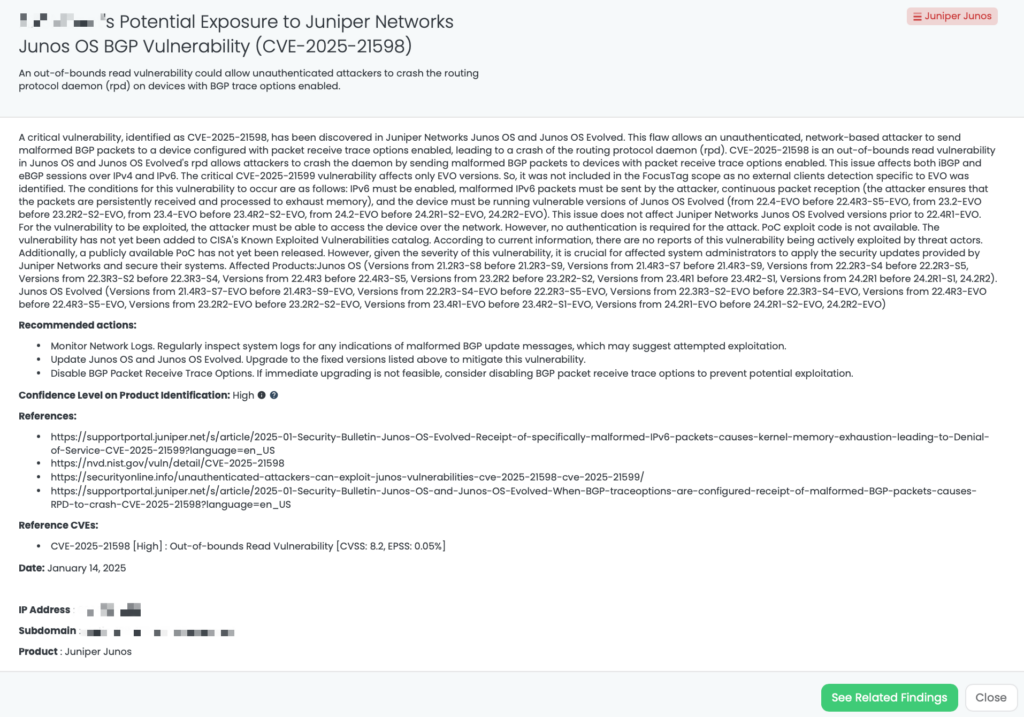
- Juniper Junos: CVE-2025-21598, Out-of-bounds Read Vulnerability in Juniper’s Junos.
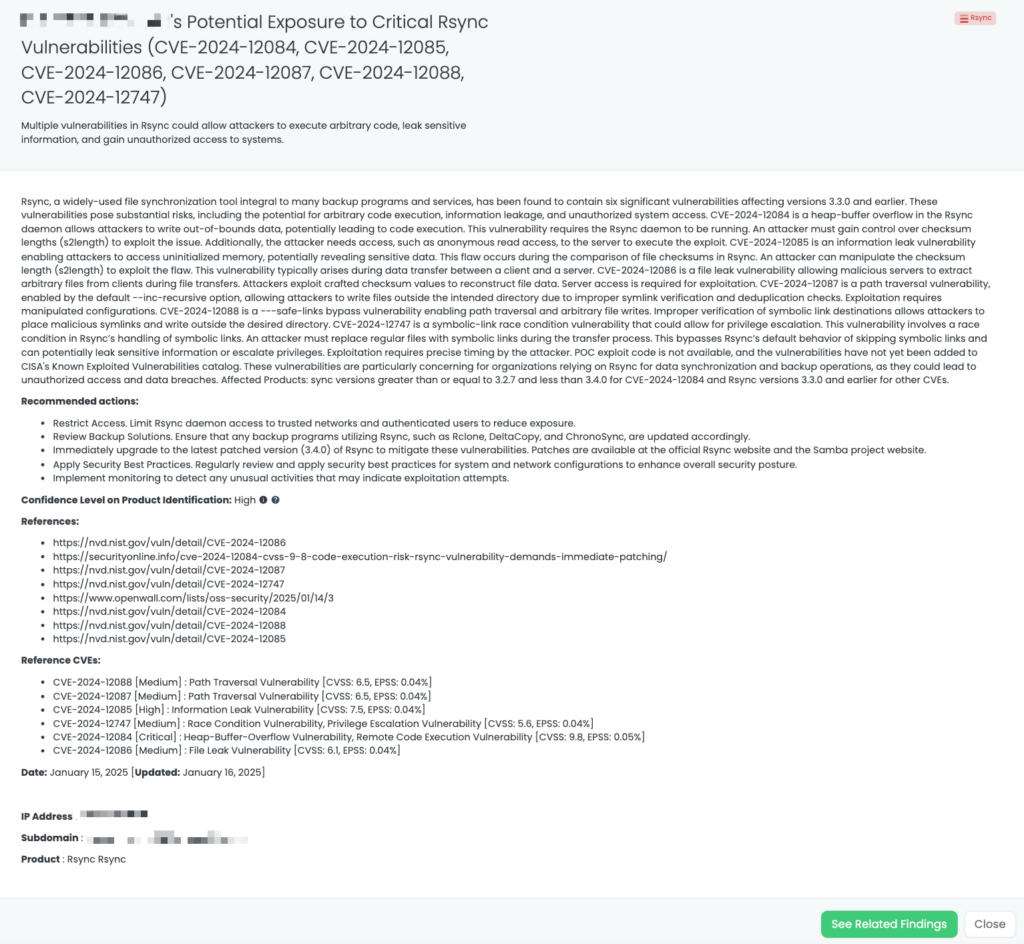
- Rsync: CVE-2024-12084, CVE-2024-12085, CVE-2024-12086, CVE-2024-12087, CVE-2024-12088, CVE-2024-12747, Heap-Buffer-Overflow Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, Information Leak Vulnerability, File Leak Vulnerability, Path Traversal Vulnerability, Race Condition Vulnerability, Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in Rsync.
- SimpleHelp: CVE-2024-57727, CVE-2024-57728, CVE-2024-57726, Unauthenticated Path Traversal Vulnerability, Arbitrary File Upload Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in SimpleHelp.
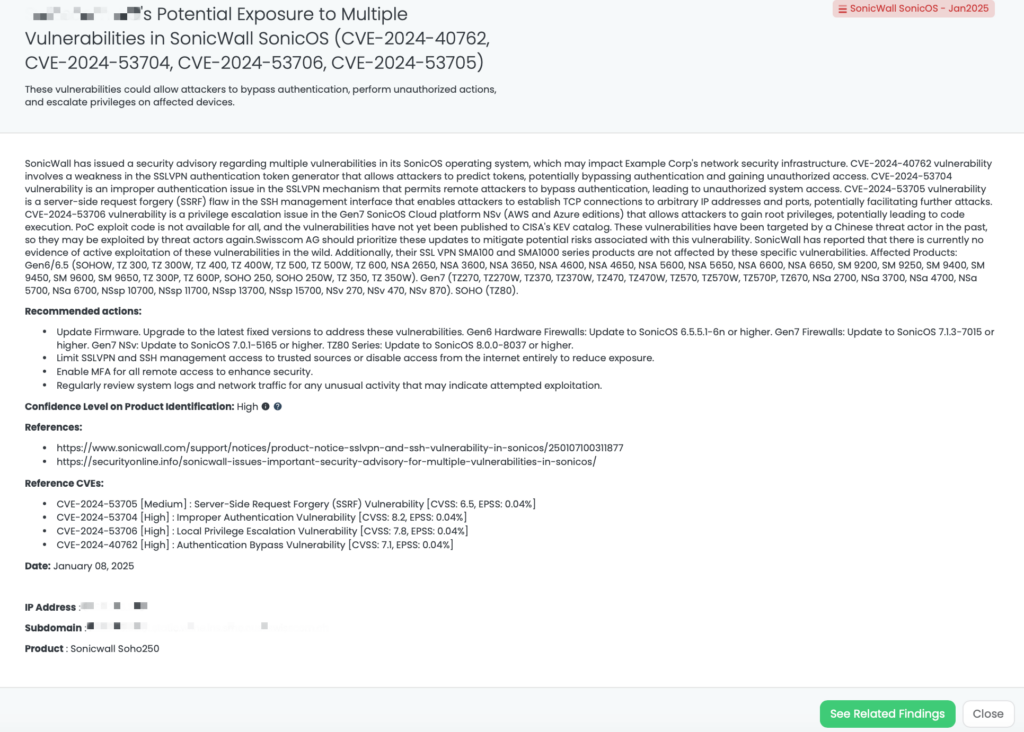
- SonicWall SonicOS – Jan2025: CVE-2024-40762, CVE-2024-53704, CVE-2024-53706, CVE-2024-53705, Use of Cryptographically Weak Pseudo-Random Number Generator (PRNG), Authentication Bypass Vulnerability, Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) Vulnerability, and Local Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in SonicWall’ SonicOS SSLVPN, SSH Management, and Gen7 Cloud NSv SSH Config Function.
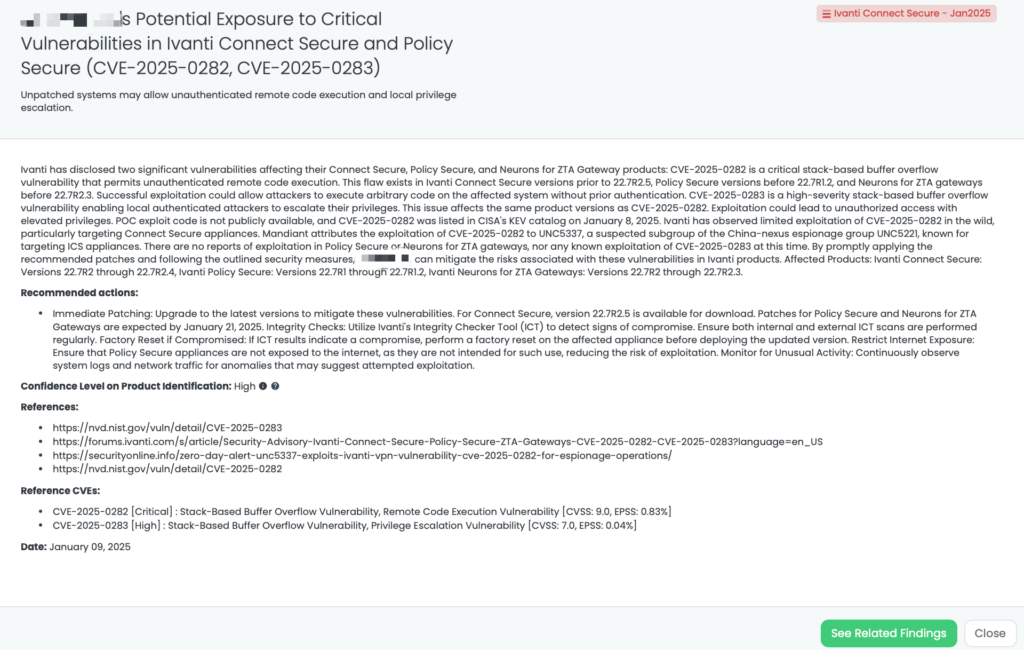
- Ivanti Connect Secure – Jan2025: CVE-2025-0282, CVE-2025-0283, Stack-Based Buffer Overflow Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and Ivanti Neurons for ZTA gateways.
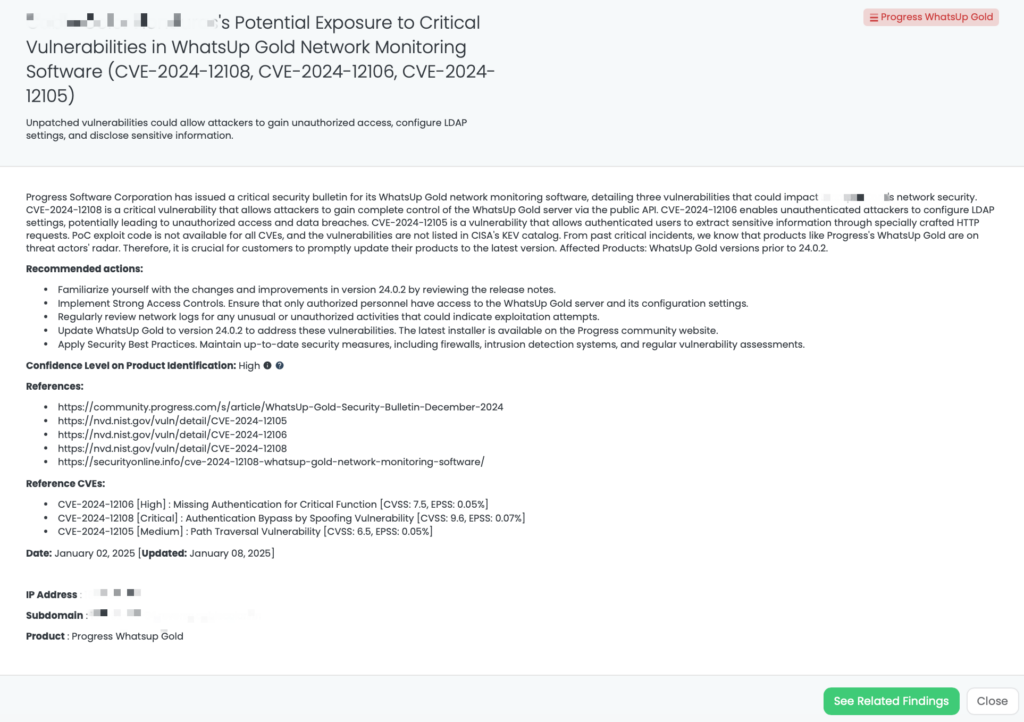
- Progress WhatsUp Gold: CVE-2024-12108, CVE-2024-12106, CVE-2024-12105, Authentication Bypass by Spoofing Vulnerability, Missing Authentication for Critical Function, and Path Traversal Vulnerability in Progress WhatsUp Gold.
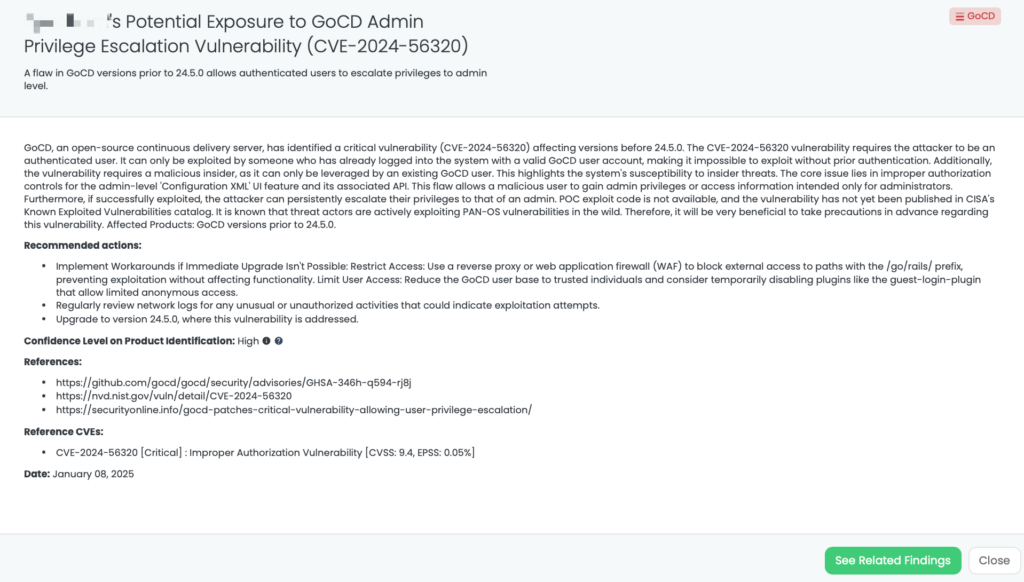
- GoCD: CVE-2024-56320, Improper Authorization Vulnerability in GoCD.
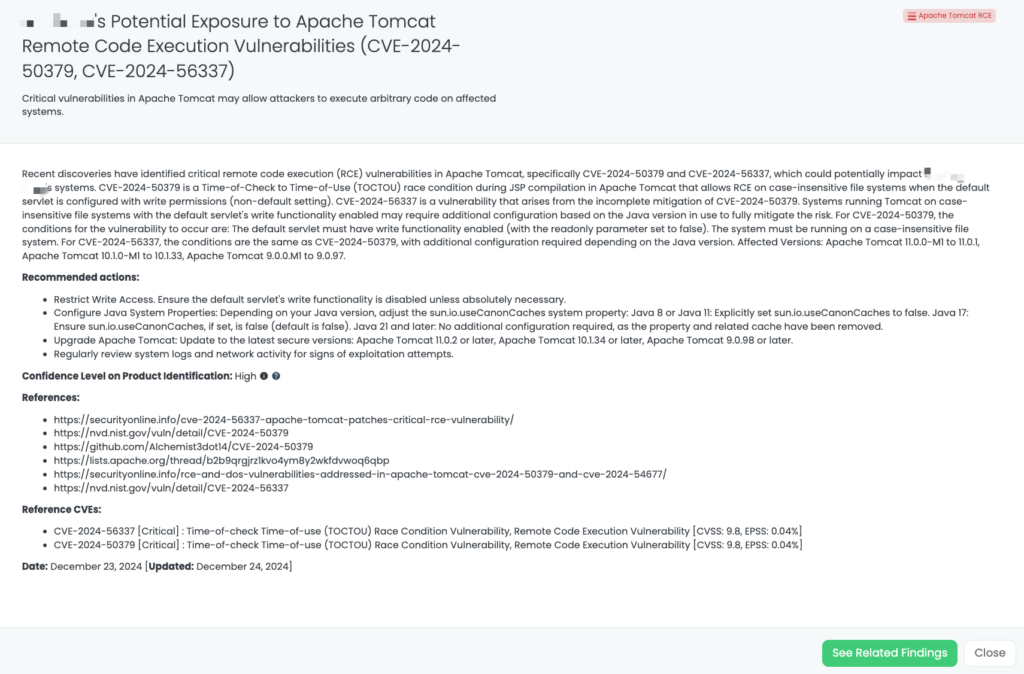
- Apache Tomcat RCE: CVE-2024-56337, CVE-2024-50379, Time-of-check Time-of-use (TOCTOU) Race Condition Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Apache Tomcat.
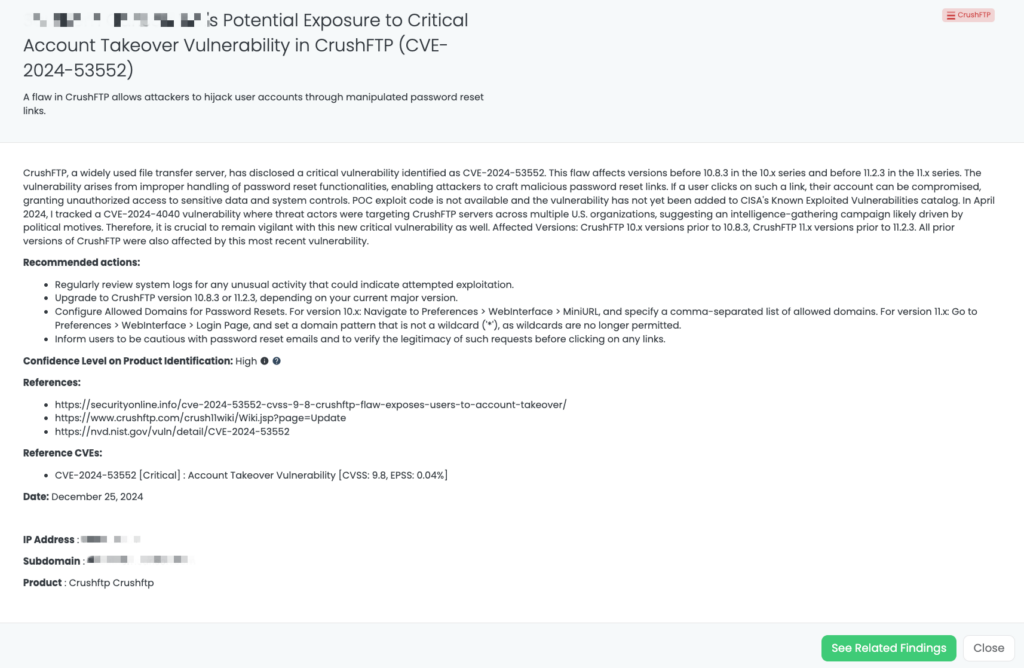
- CrushFTP: CVE-2024-53552, Account Takeover Vulnerability in CrushFTP.
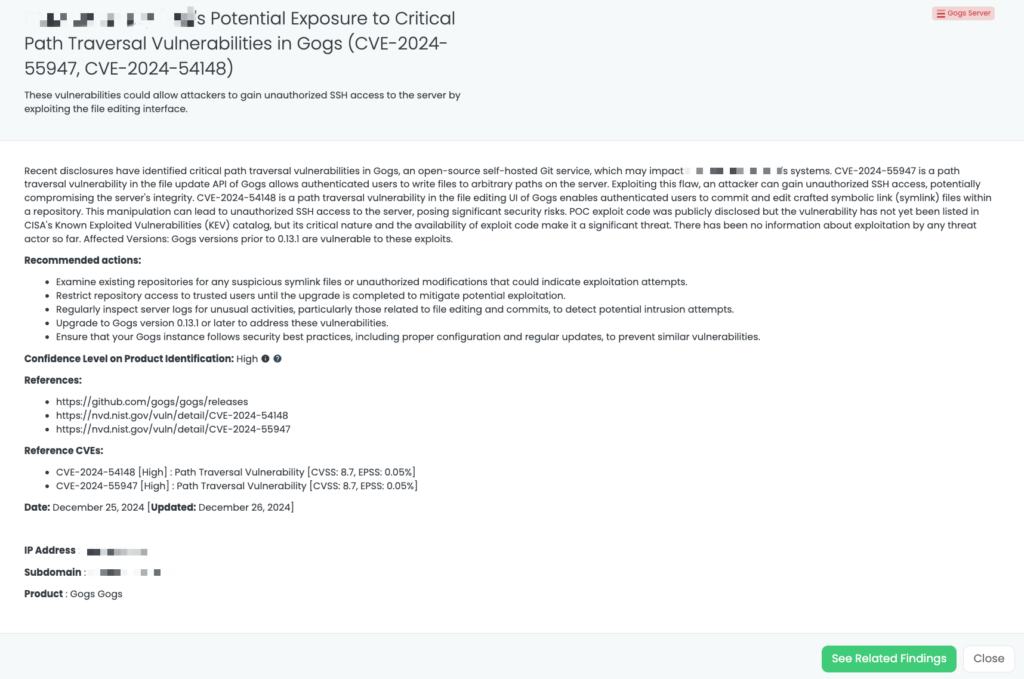
- Gogs Server: CVE-2024-55947, CVE-2024-54148, Path Traversal Vulnerability in Gogs Server.
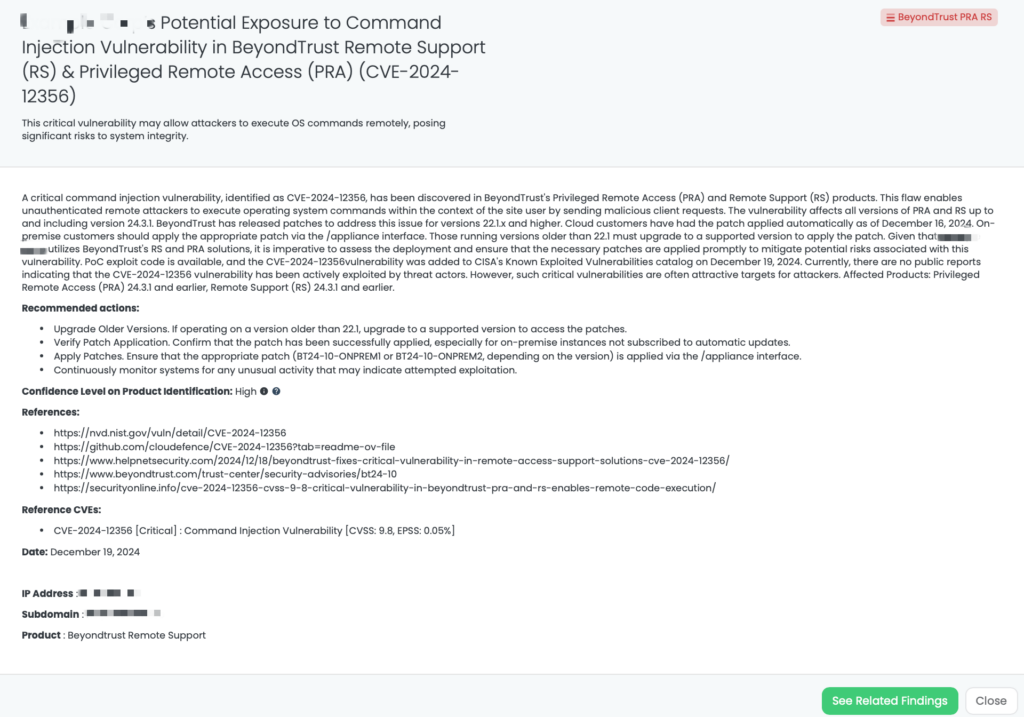
- BeyondTrust PRA RS: CVE-2024-12356, Command Injection Vulnerability in BeyondTrust’s Privileged Remote Access (PRA), Remote Support (RS).
References
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-0108
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-0110
https://security.paloaltonetworks.com/CVE-2025-0108
https://security.paloaltonetworks.com/CVE-2025-0110
https://slcyber.io/blog/nginx-apache-path-confusion-to-auth-bypass-in-pan-os
https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/KB29805?language=en_US
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-22467
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-10644
https://wiki.zimbra.com/wiki/Zimbra_Releases/10.0.12#Security_Fixes
https://wiki.zimbra.com/wiki/Zimbra_Releases/10.1.4#Security_Fixes
https://wiki.zimbra.com/wiki/Zimbra_Security_Advisories
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-25064
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-22604
https://github.com/Cacti/cacti/security/advisories/GHSA-c5j8-jxj3-hh36
https://securityonline.info/cve-2025-22604-cvss-9-1-remote-code-execution-flaw-in-cacti-poc-released
The post Focus Friday: Addressing Third-Party Risks in PAN-OS, Ivanti Connect Secure, Zimbra, and Cacti Vulnerabilities appeared first on Black Kite.