NASA Space Tech’s Favorite Place to Travel in 2025: The Moon!
NASA Space Tech’s Favorite Place to Travel in 2025: The Moon!
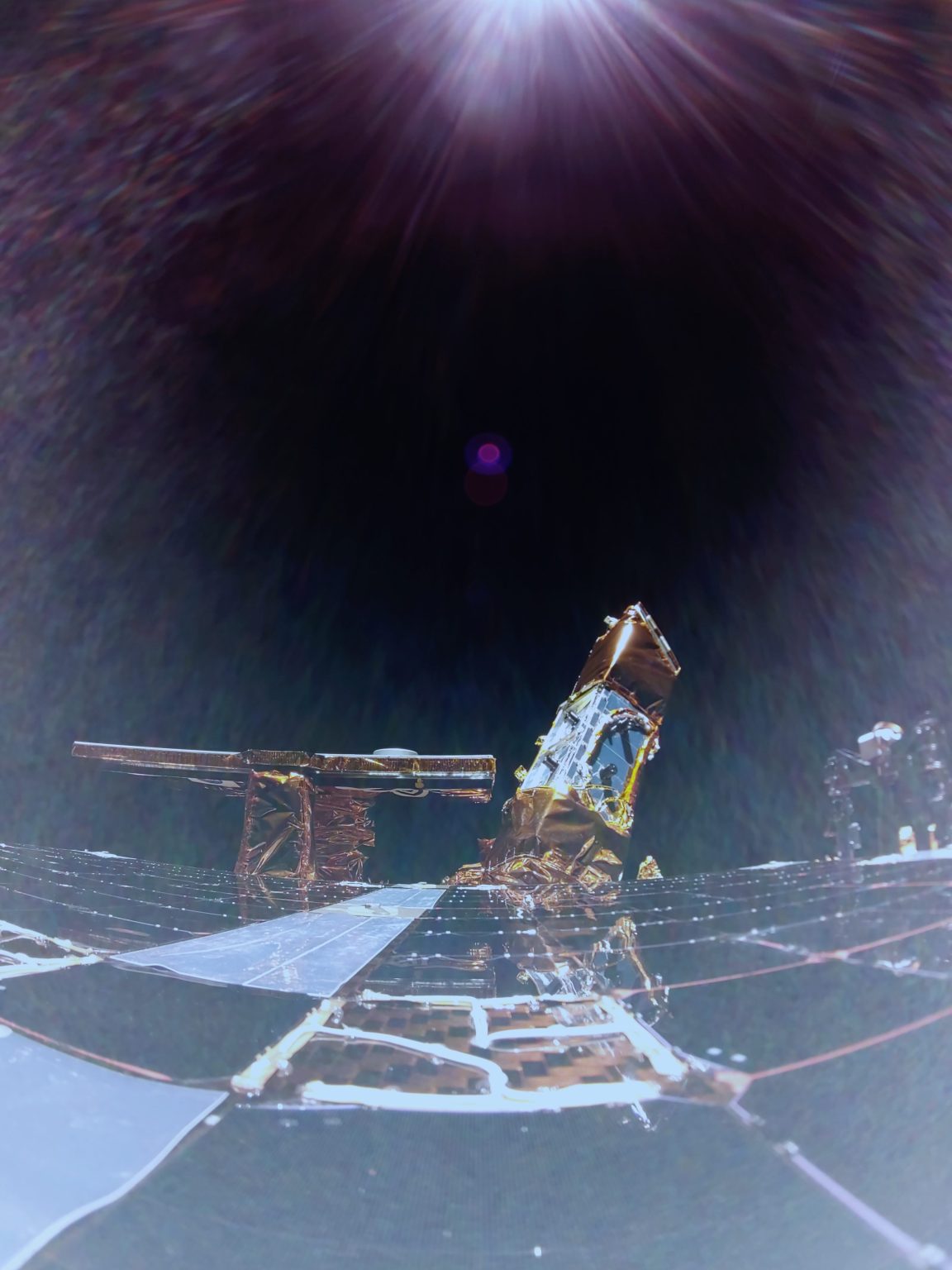

NASA Space Technology has big travel plans for 2025, starting with a trip to the near side of the Moon!
Among ten groundbreaking NASA science and technology demonstrations, two technologies are on a ride to survey lunar regolith – also known as “Moon dust” – to better understand surface interactions with incoming lander spacecraft and payloads conducting experiments on the surface. These dust demonstrations and the data they’re designed to collect will help support future lunar missions.
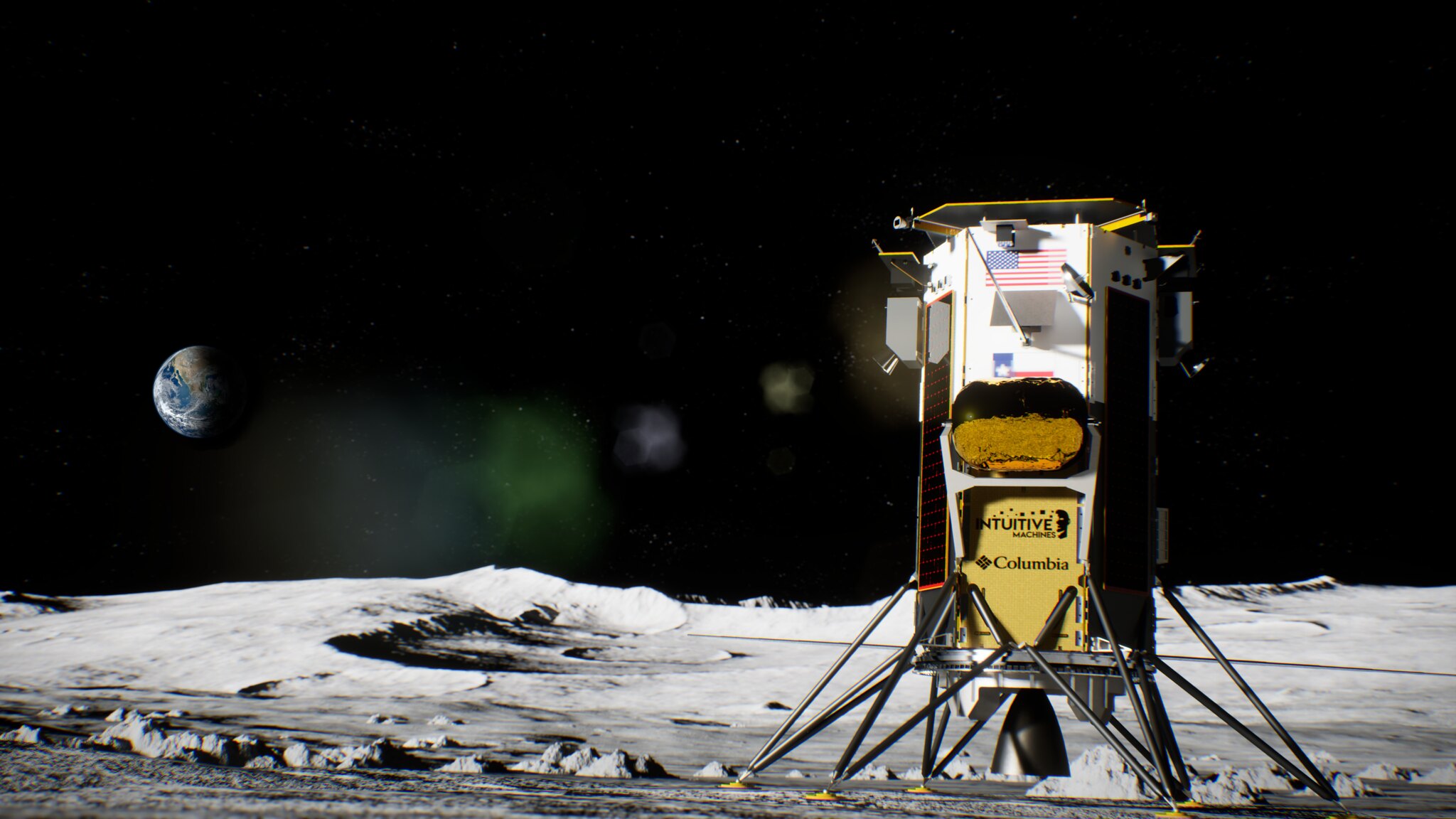
Blue Ghost Mission 1 launched at 1:11 a.m. EST aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The company is targeting a lunar landing on Sunday, March 2.
NASA Space Technology on Blue Ghost Mission 1
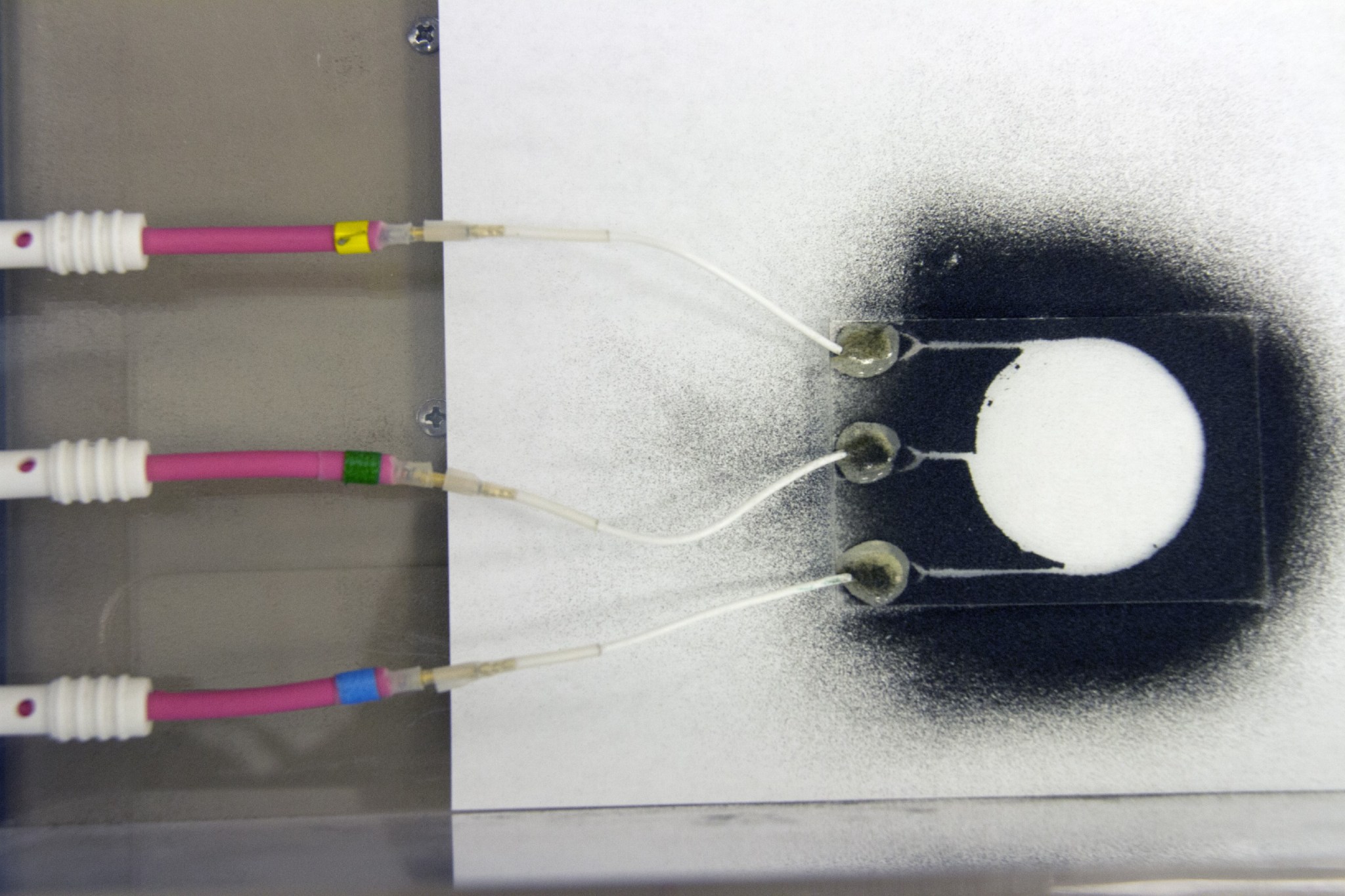
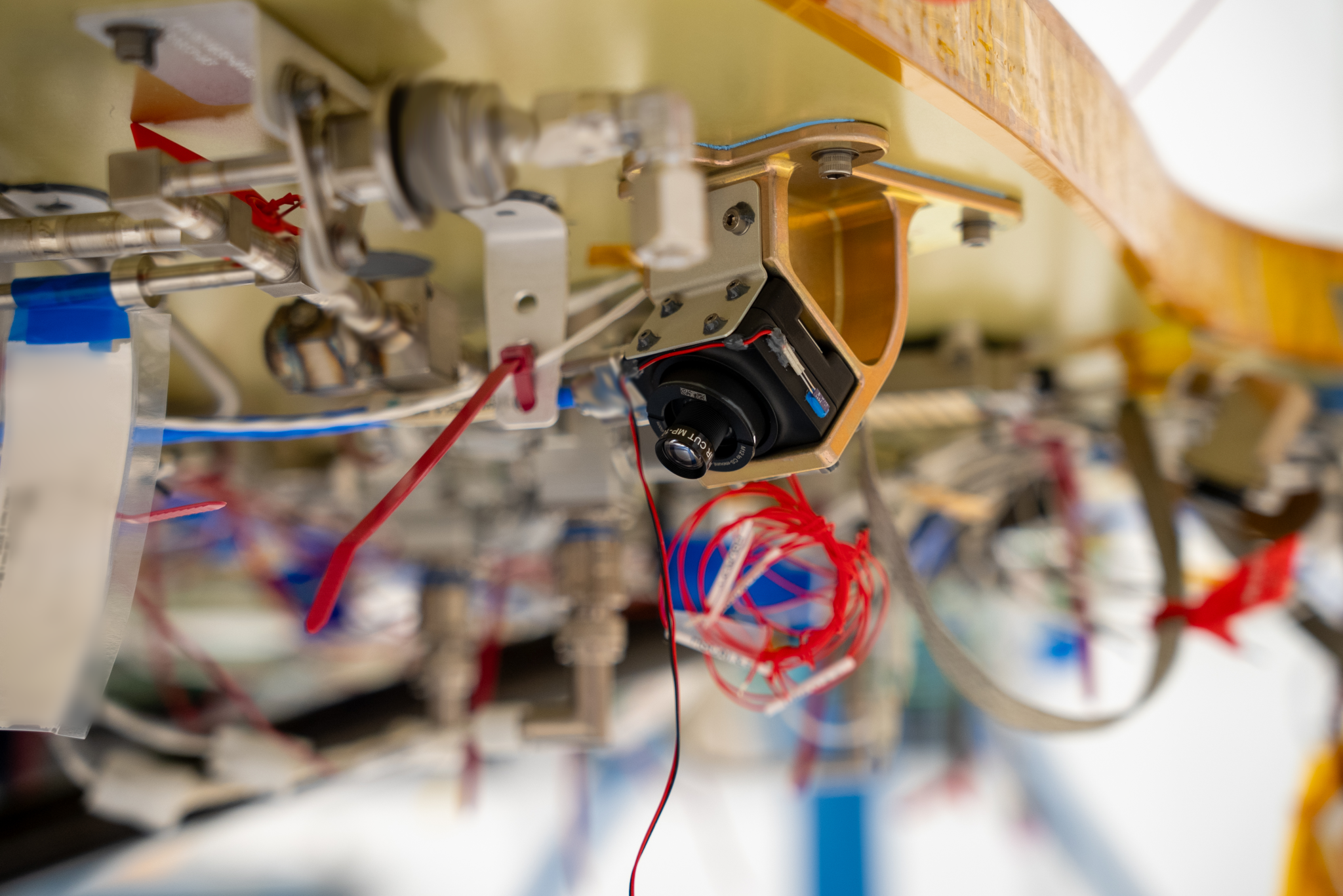
NASA’s Electrodynamic Dust Shield (EDS) will lift, transport, and remove particles using electric fields to repel and prevent hazardous lunar dust accumulation on surfaces. The agency’s Stereo Camera for Lunar Plume-Surface Studies (SCALPSS) technology will use stereo imaging to capture the impact of rocket plumes on lunar regolith as the lander descends to the Moon’s surface, returning high-resolution images that will help in creating models to predict regolith erosion – an important task as bigger, heavier payloads are delivered to the Moon in close proximity to each other.
The EDS and SCALPSS technologies will be delivered to the Moon on Firefly’s first Blue Ghost mission, named Ghost Riders in the Sky, as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. Its landing target is a 300-mile-wide basin located on the Moon’s near side, called Mare Crisium – a large, dark, basaltic plain that filled an ancient asteroid impact. First-of-their-kind experiments will deploy after landing to gather important data in a broad spectrum of areas including geophysical characteristics, global navigation, radiation tolerant computing, and the behavior of lunar regolith.
Replicating the Moon’s harsh environment on Earth is a significant challenge because of extreme temperatures, low gravity, radiation, and dusty surface. The CLPS initiative provides unprecedented access to the lunar surface, allowing us to demonstrate technologies in the exact conditions they were designed for. Missions like Blue Ghost Mission 1 are a true game changer for NASA technology advancement and demonstration.”

Michael Johansen
Flight Demonstrations Lead for NASA’s Game Changing Development program
Understanding regolith
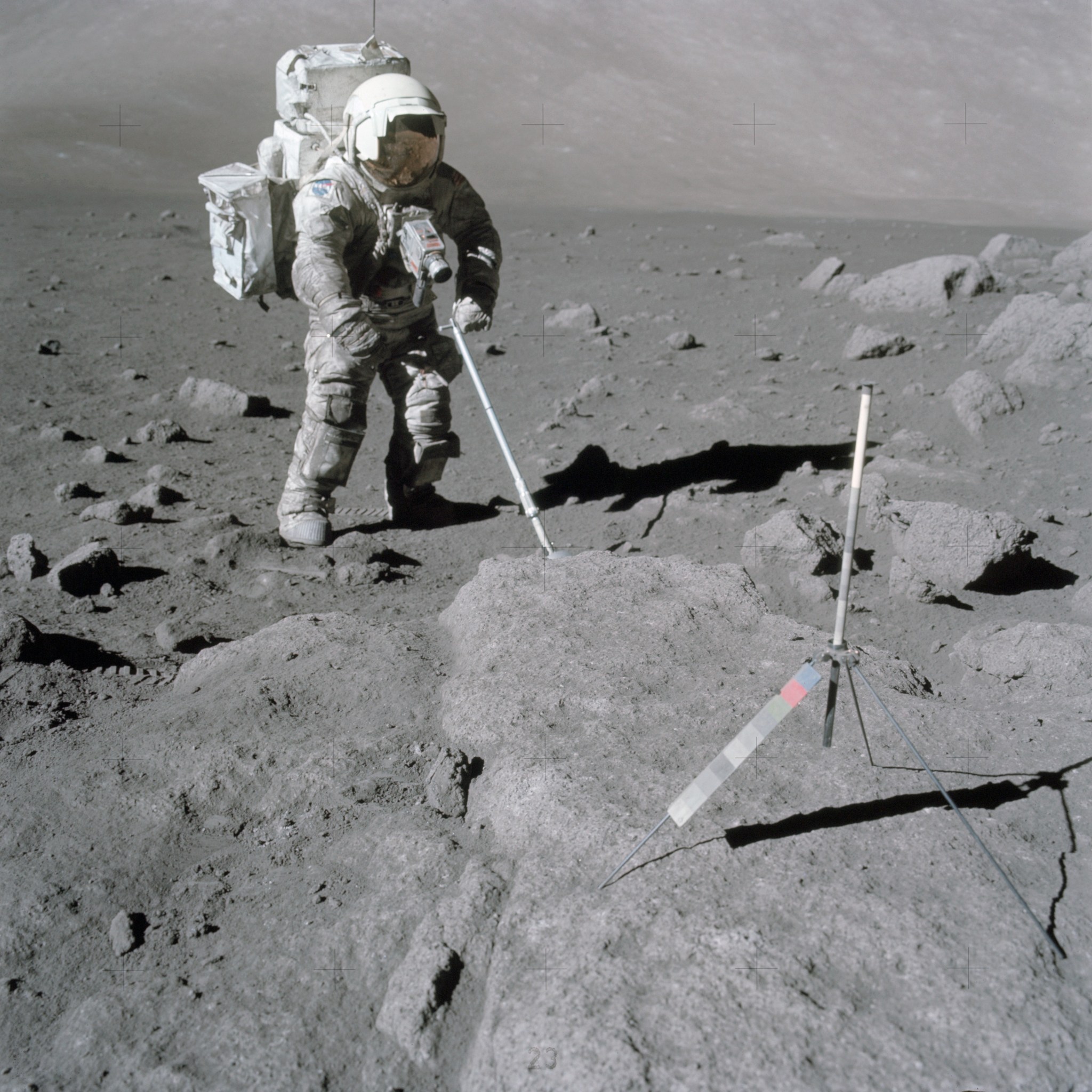
The Moon’s dusty environment was one of the greatest challenges astronauts faced during Apollo Moon missions, posing hazards to lunar surface systems, space suits, habitats, and instrumentation. What was learned from those early missions – and from thousands of experiments conducted on Earth and in space since – is that successful surface missions require the ability to eliminate dust from all kinds of systems. Lunar landings, for example, cause lunar dust to disperse in all directions and collect on everything that lands there with it. This is one of the reasons such technologies are important to understand. The SCALPSS technology will study the dispersion of lunar dust, while EDS will demonstrate a solution to mitigate it.
Getting this new data on lunar regolith with be pivotal for our understanding of the lunar surface. We’ve long known that lunar dust is a huge challenge. The Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative has enabled us to initiate lunar dust mitigation efforts across the agency, working with industry and international partners. The lunar science, exploration, and technology communities are eager to have new quantitative data, and to prove laboratory experiments and develop technology solutions.”

Kristen John
Technical Integration Lead for NASA’s Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative (LSII)
Dust mitigation technology has come a long way, but we still have a lot to learn to develop surface systems and infrastructure for more complex missions. LSII is actively engaged in this effort, working with the lunar community across sectors to expand knowledge and design new approaches for future technologies. Working alongside the Lunar Surface Innovation Consortium, LSII has a unique opportunity to take a holistic look at dust’s role in the development of surface infrastructure with other key capability areas including in-situ resource utilization, surface power, and surviving the lunar night.
Learning from the the Moon benefits Mars science and exploration
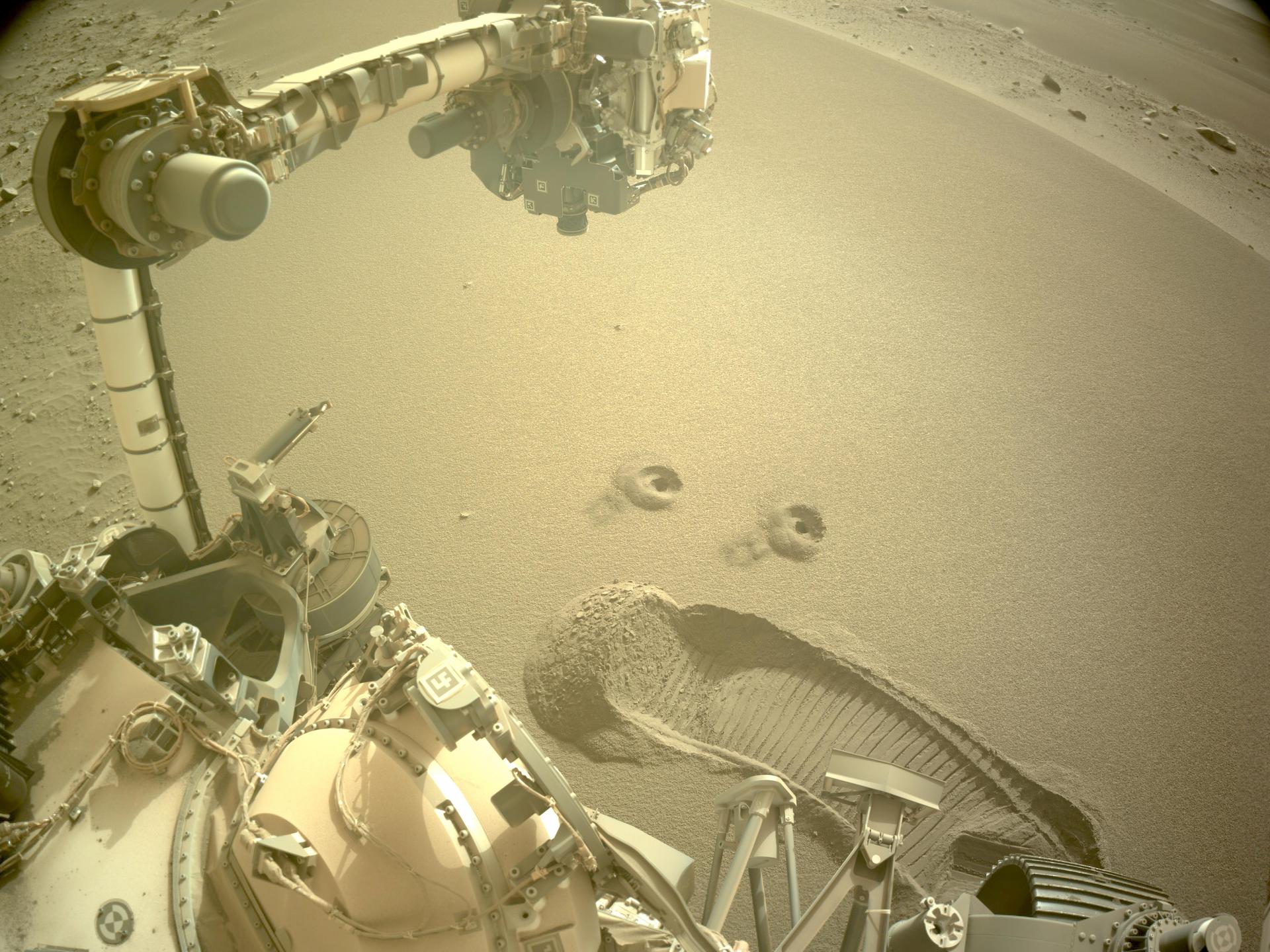
Capabilities for minimizing dust interaction are as important for future missions on Mars as it is for missions on the Moon. Like the Moon, Mars is also covered with regolith, also called Martian dust or Martian soil, but the properties are different than lunar regolith, both in shape and mineralogy. The challenges Mars rovers have encountered with Martian regolith have provided great insight into the challenges we will face during lunar surface missions. Learning is interwoven and beneficial to future missions whether hundreds of thousands of miles from Earth, on the Moon, or millions, on Mars.
Learn more from a planetary scientist about how science factors into lunar dust mitigation technologies:
Explore More
Discover More Topics From NASA
Space Technology Mission Directorate

NASA’s Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative

Game Changing Development Projects
Game Changing Development projects aim to advance space technologies, focusing on advancing capabilities for going to and living in space.

Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS)
The goal of the CLPS project is to enable rapid, frequent, and affordable access to the lunar surface by helping…